Key takeaways:
- DNS filtering provides proactive protection by blocking malicious or unwanted websites at the DNS lookup stage.
- Beyond threat prevention, DNS filtering benefits businesses by enhancing productivity and aiding regulatory compliance.
- DNS filtering is a line of defense that complements, rather than replaces, other security tools like firewalls and antivirus software.
Firewalls and antivirus software are solid defenses for your site. However, they don’t provide complete protection against all threats. When looking for another layer of defense, you can count on DNS filtering to protect your site from the roots.
DNS filtering is a cybersecurity layer that stops harmful websites at the DNS lookup stage, blocking malicious content before it loads. In this article, you’ll learn more about it and how it can protect your business from online risks and boost employee productivity.
What is DNS filtering?
To grasp DNS filtering, it’s helpful to understand the Domain Name System (DNS) role in the process. The Internet is made up of many websites, each with a unique numerical address (an IP address). Since remembering long strings of numbers is impractical, we use domain names (like networksolutions.com) to access websites.
The DNS acts like the Internet’s phonebook. When you look up a domain name, the browser connects to a DNS server to retrieve the domain’s corresponding IP address. Once it finds the IP address, your browser can connect to the website.
DNS filtering works within the process by inspecting requests against pre-defined policies or blocklists. If a request connects to a malicious or unauthorized website, the DNS filter intercepts and stops the connection. With DNS filtering, your network can block threats like malware, ransomware, and phishing attempts before they reach you.
How does DNS filtering work?
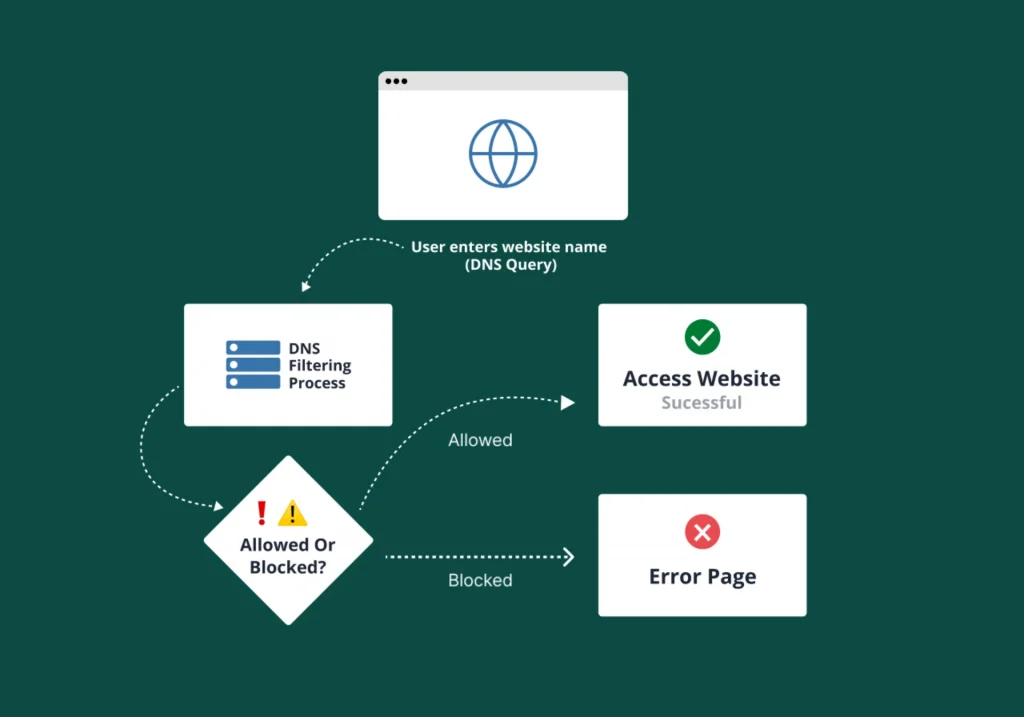
It operates by inspecting domain name requests for network safety and policy enforcement. Here’s a breakdown of the typical workflow:
- DNS query initiation
- Redirection to filter
- Policy evaluation (blocklist, allowlist and categorization)
- Action based on policy
- Logging and reporting
Let’s get into the details of each process.
DNS query initiation
When users try to access a website, their device sends a DNS query to a configured DNS server.
Redirection to filter
The network’s configuration directs the query to a specialized DNS filtering server instead of establishing a direct connection.
Policy evaluation
The filtering service then checks the requested domain name against its extensive databases and the organization’s pre-defined policies. These databases include:
- Blocklists. These are long lists of known security risks such as:
- Malicious sites: malware hosts, phishing scams, command-and-control servers
- Undesirable content categories: adult content, gambling sites
- Unproductive sites: social media, streaming services
- Allowlists (whitelists). These contain domains that are always permitted, regardless of other policies, due to business applications.
- AI/Machine learning categorization. Advanced solutions use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to categorize new and emerging domains in real time. These help in identifying newly created threats not listed yet in traditional blocklists.
Action based on policy
- Allowed. If the system detects a safe and compliant website, the filter resolves the domain name, and the website loads normally.
- Blocked. If the domain is on a blocklist or violates a policy, the filter prevents the connection. The network might redirect the user to a block page, or the connection simply times out.
Logging and reporting
DNS filtering services log all requests, resolutions, and blocks throughout this process. The data gathered in this step logs all attempted malicious connections, policy violations, and overall internet usage.
How do you set up DNS filtering?
It can be implemented in several ways, depending on your network structure and user needs (including remote workers).
- Cloud DNS services. You configure your network’s routers or individual devices to use a third-party cloud-based DNS filtering service. The filter routes all DNS queries from your network through their servers.
- Router or DNS server-level filtering. You can configure your primary network router or internal DNS servers for on-premises solutions.
- Endpoint agent installation. Businesses can use an endpoint agent for devices that frequently operate outside the corporate network, such as laptops or mobile devices. The endpoint agent ensures all DNS requests from devices pass through the filtering service, regardless of location.
How do you effectively implement DNS filtering?
It might seem complicated. But with a straightforward implementation plan, you can set it up without a fuss. Here’s what you need to do.
- Create clear policies. Define clear, specific filtering policies based on different user groups or departments.
- Prevent bypasses. Ensure users can’t easily bypass the filter (e.g., manually changing DNS settings on their devices).
- Route internal DNS. Consider routing internal DNS queries through your filtering solution for better visibility and logging.
- Test and iterate. Roll out policies gradually and test them to avoid blocking legitimate business tools. Review logs regularly and adjust policies as needed.
Why should businesses use DNS filtering?
DNS filtering offers an inclusive defense against various cyber threats and operational challenges, making it useful for modern businesses such as yours. Here are more reasons why businesses can benefit from it:
- Malware and ransomware prevention
- Phishing protection
- Enhanced productivity
- Compliance and data security
- Remote work and hybrid workforce scalability
- Advanced AI-based threat detection
- Reduced security burden
- Improved network performance
Malware and ransomware prevention
DNS filtering is a key protective measure against malware and other exploit kits. It blocks malicious domains and stops the initial connection, preventing harmful payloads. You can learn more about malware prevention methods in our malware prevention guide.
Phishing protection
It can block access to known phishing sites, protecting employees from scams that steal credentials.
Enhanced productivity
By restricting access to non-work-related websites during business hours, it helps reduce distractions and improve employee productivity.
Compliance and data security
Many regulatory frameworks, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), require solid security measures. DNS filtering helps businesses stay compliant by preventing data breaches by malicious websites.
Remote work and hybrid workforce scalability
DNS filtering, especially with endpoint agents, extends protection to off-network devices, ensuring consistent security regardless of location.
Advanced AI-based threat detection
Modern DNS filtering uses AI and machine learning to identify and block new, emerging threats not cataloged by traditional signature-based systems. AI integration helps reduce false positives while neutralizing novel threats.
Reduced security burden
By automatically blocking threats at the DNS level, it reduces the volume of malicious traffic reaching other security layers.
Improved network performance
Blocking unwanted or malicious domains can speed up connections by reducing unnecessary traffic and bandwidth consumption.
DNS filtering vs. other security tools
While DNS filtering is powerful, it complements, rather than replaces, other cybersecurity tools.
DNS filtering vs. web filtering
- DNS filtering operates at the DNS lookup stage, blocking connections based on domain names before establishing a full connection.
- Web filtering typically operates at the HTTP/HTTPS (application) layer, inspecting web page content once a connection is made. It can analyze page content, scripts, and downloaded files in more detail.
DNS filtering vs. firewalls
- Firewalls act as barriers, controlling traffic and blocking unauthorized access based on IP addresses and protocols.
- DNS filtering blocks malicious or unwanted domains at the DNS resolution stage. They work in tandem: firewalls protect the network perimeter, while DNS filtering proactively protects against specific web-based threats.
DNS filtering vs. antivirus software
- Antivirus (AV) software requires installation on each endpoint. It detects and removes malicious software that has already landed on a device.
- DNS filtering proactively prevents malware from reaching the endpoint by denying access.
DNS filtering vs. content filtering
- Content filtering is a broader term for systems regulating access to web content. DNS filtering can be a component of content filtering, which might also involve deep packet inspection for detailed content analysis.
DNS filtering provides a dependable first line of defense by preventing connections to known bad internet neighborhoods. It complements other tools by reducing the volume of threats, making online defenses more efficient and effective.
If you’re using WordPress, you can find specific network security tips in our WordPress best security practices guide.
Tighten your network’s security with Network Solutions
Whether you’re a small business owner or a large enterprise, it’s prudent to include a DNS filtering system in your security strategy. It helps block harmful content and protect your overall network.
If you’re looking to tighten your defense, contact Network Solutions today to discover security solutions custom-made for you. We offer comprehensive website security features that keep your website shielded from malicious activity.
From initial setup to consultation, we’re here to help secure your network and empower your business to operate safely online.
Frequently asked questions
DNS filtering is primarily used to block access to malicious websites, unwanted content categories (such as adult or gambling sites), and unproductive websites (e.g., social media) at the domain name resolution stage.
While it’s an excellent first line of defense against malware, it’s not enough on its own. A robust cybersecurity strategy also includes additional security services, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and employee cybersecurity training.
Modern DNS filtering services are designed to operate with minimal to no impact on internet speed. It can improve network performance by blocking unwanted connections and reducing unnecessary traffic.
Remote and mobile devices can be covered by installing a lightweight endpoint agent directly on them. The agent ensures all DNS queries from that device are routed through the DNS filtering service, regardless of the connection type.




