Key takeaways:
- Google Search Console (GSC) helps you track clicks, impressions, and rankings to improve SEO.
- Use GSC to fix indexing issues and boost your site’s visibility on Google.
- Combine GSC with GA4 for better insights into search performance and user behavior.
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool from Google that provides a clear picture of how your website performs in search results. It offers insights to track performance, identify issues, and improve rankings, all without requiring technical expertise. GSC is a vital tool for marketers, small business owners, and SEO professionals.
With GSC, you can view which search terms drive organic traffic to your site, how often your pages appear in search results, and how many clicks they receive. This data helps you optimize your site for better visibility.
Additionally, GSC helps fix technical issues, address indexing problems, and track rankings over time. Its widespread use among SEO professionals speaks of its importance in modern SEO workflows.
If your goal is to improve your Google visibility, GSC is a great place to start.
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a reporting tool that shows how your website performs in Google Search. It helps you understand how often your pages appear in search results, which search terms trigger them, and how many people click through to your site.
GSC tracks only organic traffic from Google Search. It does not include visits from Bing, paid ads, social media, or email campaigns.
Note: The numbers presented are fictional and for illustration purposes only.
Here are key metrics you’ll find in GSC:
- Total clicks: How many times someone clicked your site from a search result.
- Total impressions: How often are your pages viewed in Google Search.
- Average CTR: The percentage of impressions that resulted in clicks.
- Average position: The average ranking of your page across all queries that it ranks for. In the query report, this refers to the average position of all pages ranking for that specific query.
GSC only reports data for pages that are indexed or eligible to appear in search results. Pages that haven’t been crawled or are blocked from indexing typically won’t appear in performance reports.
Note: Reports are delayed by 2–3 days and may be sampled when query volume is very low. That means the numbers you see aren’t real-time, but they’re close enough to help you make informed decisions.
GSC vs. GA4: What’s the difference?
Google Search Console (GSC) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) are two tools from Google. They both help you understand how your website is performing, but they focus on different things.
GSC shows how your site performs in Google Search results. Meanwhile, GA4 tracks what users do when they land on your site.
If you want to know how people find you in search, use GSC. If you want to know what they do after they click, use GA4. Many site owners use both tools together.
How Google Search Console compares to GA4
These tools work best when used together, but it’s important to understand what each one is designed to do. The table below shows the main differences between Google Search Console and GA4 at a glance:
| Feature | Google How Google Search Console compares to GA4 Search Console (GSC) | Google Analytics 4 (GA4) |
| Traffic source | Google Search only | All traffic sources (search, social, ads) |
| Purpose | Search performance and indexing | On-site user behavior and engagement |
| Main metrics | Clicks, impressions, CTR, position | Sessions, events, bounce rate, conversions |
| Tracks post-click activity | No | Yes |
| Site variations (https, www) | Treated as separate properties | Combined into one view |
| GSC integration | Can be linked to GA4 | Shows GSC data in select GA4 reports |
GSC now supports integration with GA4, so you can see your search traffic data alongside your site engagement metrics. This makes it easier to connect how users find your site with what they do once they arrive.
Note: Google Search Console does not track what users do after they land on your site — such as how long they stay, what pages they visit, or whether they convert. For that kind of insight, use GA4.
How to set up Google Search Console
Before you can use Google Search Console (GSC), you need to add your website and prove that you own it. This lets Google show you detailed search data and indexing reports for your site.
The setup process is simple, but each step plays an important role in how data is collected and reported.
Note: Depending on your access permissions and limitations, you may not be able to view or edit certain settings.
Here’s how to get started:
Step 1: Add your property
When you first open GSC, you’ll be asked to add a new property. This means registering your website in the tool.
You’ll choose between two property types:
- Domain property (recommended):
Covers everything under your domain — all subdomains and both http and https versions.- Example: adding yourdomain.com includes https://www.yourdomain.com, http://blog.yourdomain.com, and any other variation.
- URL prefix property:
Tracks only the exact URL you enter.- Example: adding https://www.yourdomain.com would not track http://yourdomain.com or other subdomains.
Pro tip: Choose the Domain property for the most complete and unified data across your entire website.
Some site owners also add each URL variant separately to compare performance or diagnose redirect issues.
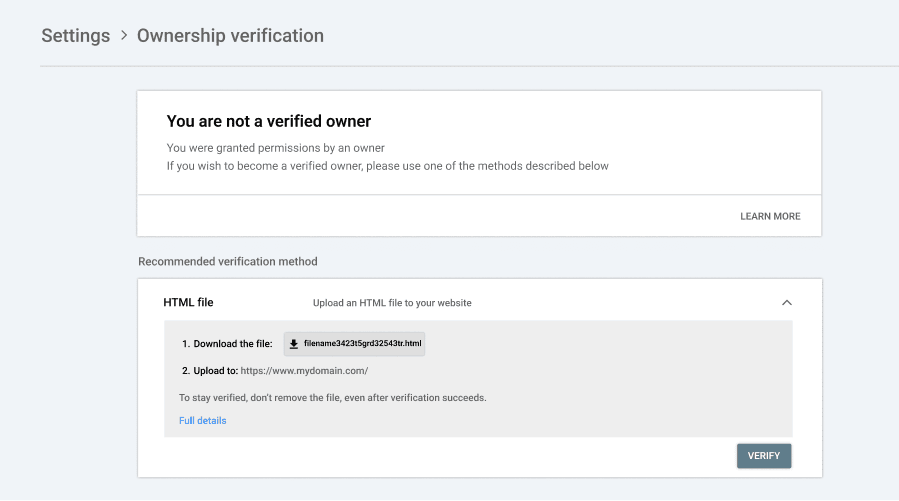
Step 2: Verify ownership
After adding your property, Google needs to verify that you have control over the site. This keeps search data private and accurate.
Note: The numbers presented are fictional and for illustration purposes only.
There are several ways to verify ownership:
- DNS record (TXT entry). Recommended for Domain properties. You’ll add a short TXT record to your domain’s DNS settings.
- HTML file upload. Download a file from Google and upload it to your site’s root directory.
- HTML <meta> tag. Paste a tag into the <head> section of your homepage.
- Google Analytics. If your GA tracking code is installed, you can use it for verification.
- Google Tag Manager. If you use GTM and have container permissions, this method may apply.
Each method is explained during setup, and you only need to complete one. You can find detailed guidance here: Verify site ownership
Step 3 (optional): Submit your sitemap
After your property is verified, you can optionally submit a sitemap to help Google find your content more efficiently.
- Go to the Sitemaps section in the left-hand menu of GSC.
- Enter the full URL of your sitemap (e.g., https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml).
- Click Submit to send it to Google.
A sitemap is especially helpful for:
- Large websites with many pages
- New sites with few backlinks
- Sites using rich media (like video or images)
- Sites with isolated or hard-to-discover pages
Although Google can find pages on its own, submitting a sitemap increases the chance that important or updated content will be crawled quickly.
For more information, see Submit a sitemap
Overview of Google Search Console reports
The Overview page in Google Search Console gives you a high-level summary of your website’s performance, indexing, user experience, and enhancement status.
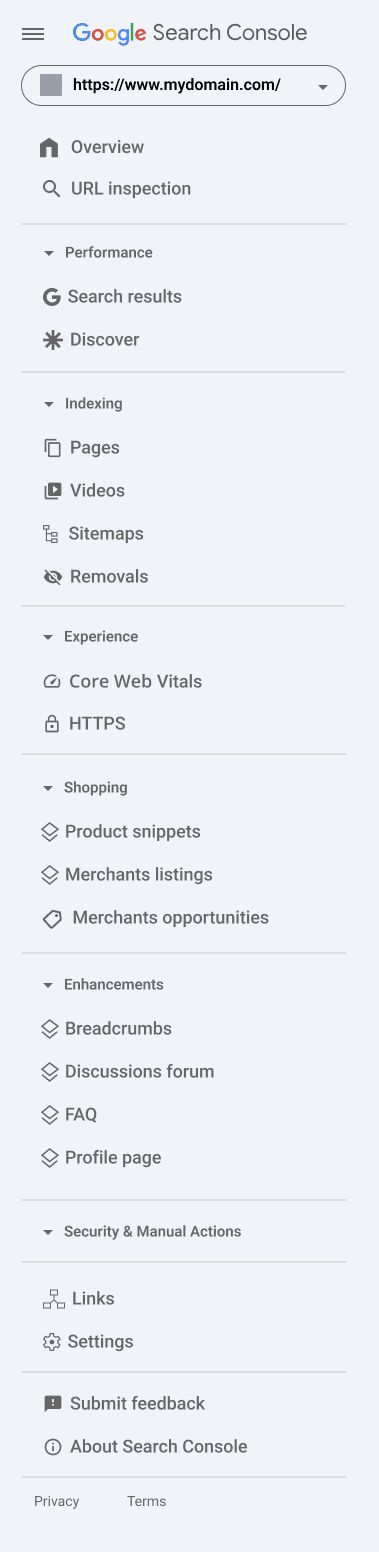
The image below show the left-side navigation panel in GSC, also known as the sidebar or dashboard menu. This is where you’ll access every major report and tool available in your property.
As previously mentioned, most reports update every 2–3 days, so the data you see may not reflect real-time activity. However, it updates often enough to support regular monitoring and data-based SEO decisions.
Here’s what each section in the sidebar represents:
Overview section
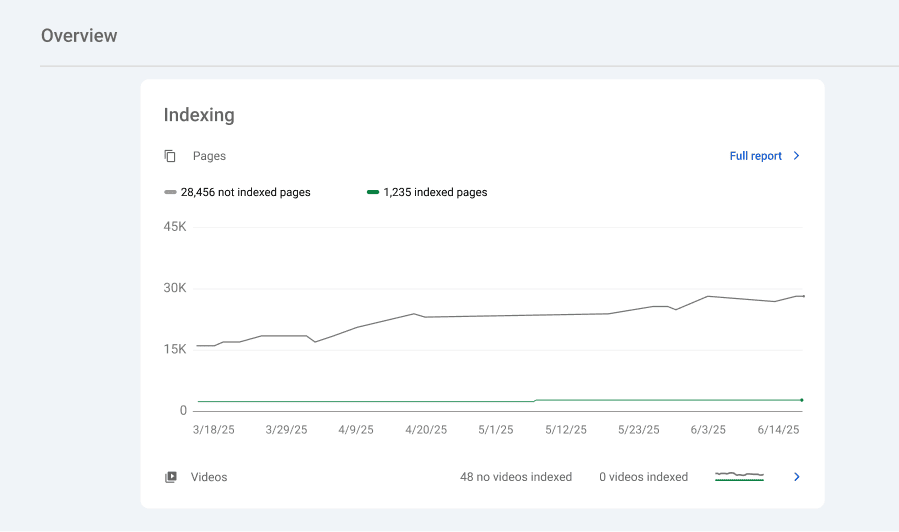
The Overview section is the first thing you see when you log in to Google Search Console. It gives a snapshot of your website’s performance, indexing status, user experience, and enhancement opportunities.
Note: The numbers presented are fictional and for illustration purposes only.
It summarizes four key areas:
- Indexing. The number of pages indexed or excluded, including pages with errors or warnings.
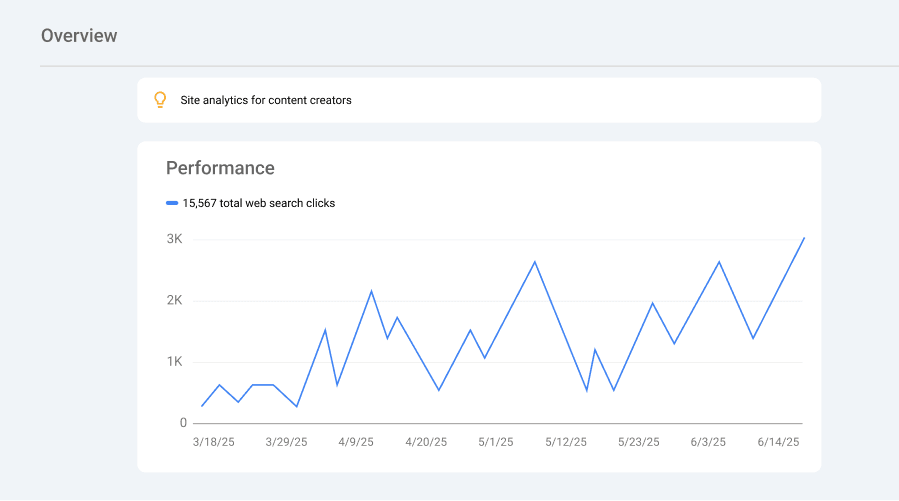
- Performance. A preview of your total clicks, impressions, and average position from Google Search.
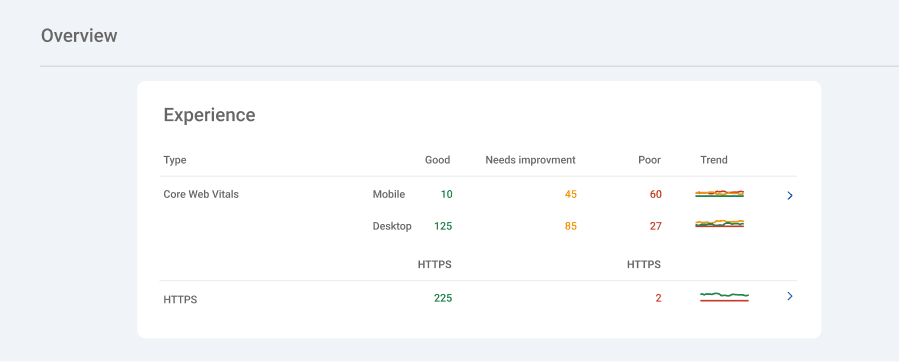
- Experience. A summary of your Core Web Vitals and mobile usability results.
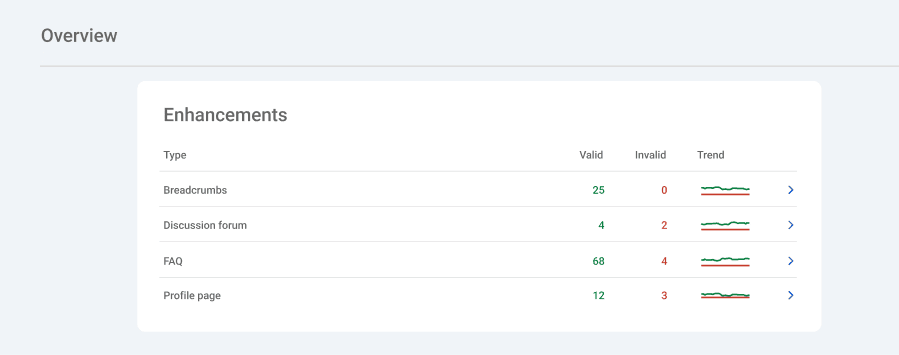
- Enhancements. Information about structured data features like FAQs, breadcrumbs, and videos.
Each box includes a “Full report” button that opens a more detailed view for deeper analysis.
What is Search Console Insights?
Search Console Insights is a feature designed to help you understand how people discover your content and what content performs best.
You can access it by clicking the “Search Console Insights” button at the top of the Overview page.
Here’s what you’ll see inside (please note that the images and numbers presented are fictional and for illustration purposes only):
- Performance on Google
- Clicks from Google Search. The total number of clicks your content received in the selected time period.
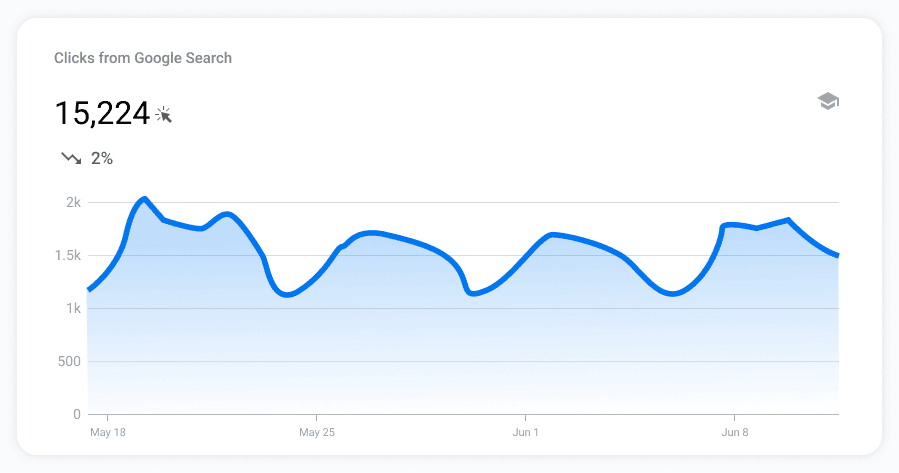
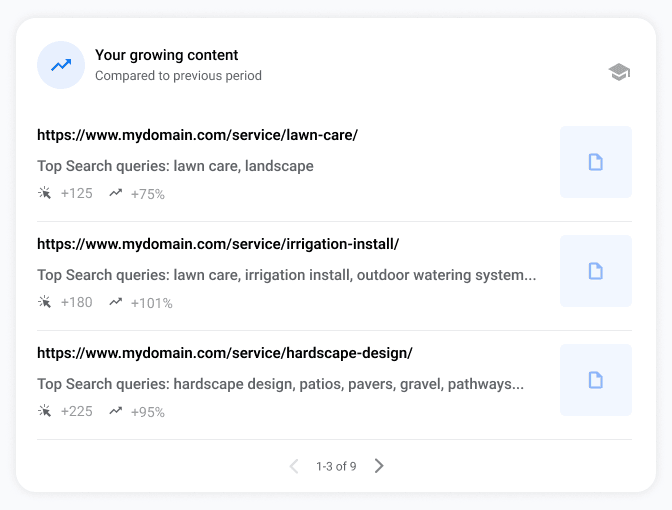
- Your growing content. Pages that have increased in search clicks compared to the previous period.
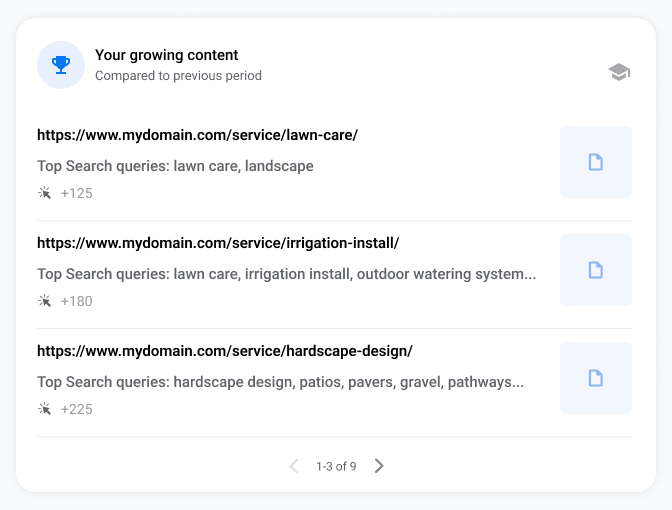
- Your most popular content. Pages with the highest number of total search clicks.
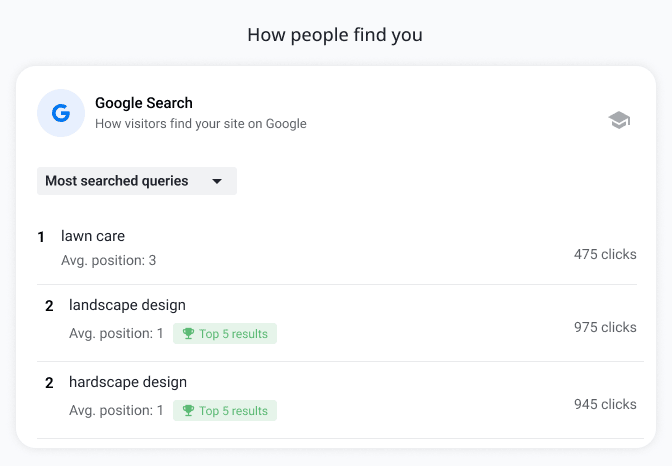
- How people find you. Insights into top-performing search queries and referring websites.
2. Achievements. Located on a separate page, this section celebrates key milestones, such as:
- A page hitting 100 total clicks
- Significant growth in page performance
- Trending pages compared to previous months
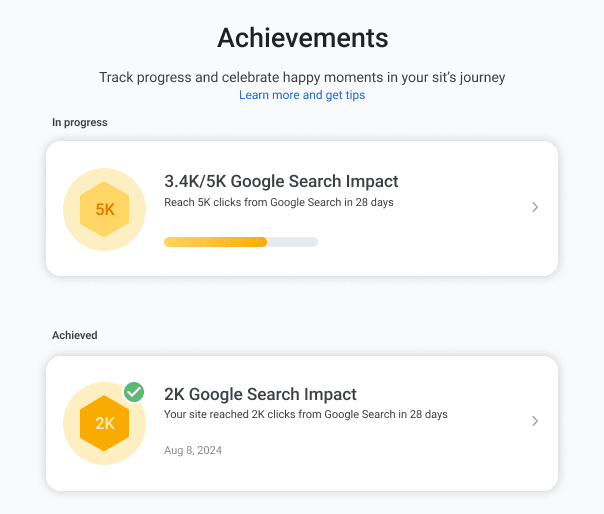
Note: These achievements are informative and motivational, but they do not impact Google rankings.
Search Console Insights combines data from Google Search Console and Google Analytics (if connected). It gives you a high-level view of how your site is performing over the past 28 days and what content is getting noticed.
What is URL inspection tool?
The URL Inspection Tool is located near the top of the left-hand menu in Google Search Console. Unlike the other reports, which summarize site-wide data, this tool focuses on one page at a time.
Use it when you want to:
- Check if a specific URL is indexed
- Understand how Google crawled it
- Request re-indexing after making changes

This tool is helpful when troubleshooting a problem with a page — especially if it’s not showing up in search or showing outdated information.
You’ll find a search bar at the top of the GSC interface. Paste the full URL of any page from your verified property and press Enter to inspect it.
Note: This tool works best for checking one page at a time. For larger performance trends or multiple URLs, use the Performance or Indexing reports.
Performance report
The Performance report is one of the most important sections in Google Search Console. It provides insights into how your website appears in Google Search and how people interact with your content once it appears in the search results.
Note: To protect user privacy and due to system limitations, the Performance report only shows the most relevant data. It omits low-frequency, sensitive, or less important queries across your property.
The Performance report is divided into two main reports:
- Search results
- Discover
Each report gives you unique insights into how your content is performing in Google Search and Google Discover.
- Search results report
The Search results report shows how your website performs in Google Search. It tracks user interactions and engagement with your site when users search for keywords or phrases on Google.
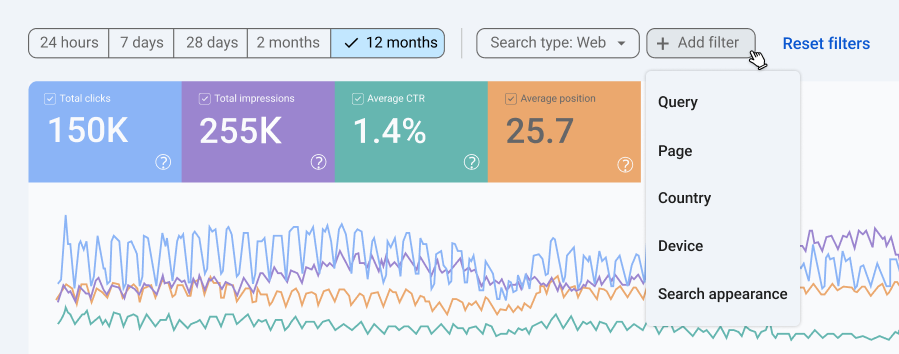
Note: The numbers presented are fictional and for illustration purposes only.
Filters and customization options in Search results:
- Date range. Choose from 24 hours, 7 days, 28 days, 3 months, or a custom range.
- Search type. Filter by Web, Image, Video, or News search data.
- Query filter. Focus on specific search terms people typed into Google.
- Page filter. View performance data for a specific page or a group of pages (e.g., all URLs containing /blog).
- Country filter. See performance by geographic region.
- Device filter. Break down performance by desktop, mobile, or tablet.
- Search appearance. View performance for special formats like:
- AMP results
- Rich results (FAQ, How-to, Reviews)
- Web stories
- Compare mode. Compare two values side by side (e.g., mobile vs desktop, current month vs last month).

Note: The numbers presented are fictional and for illustration purposes only.
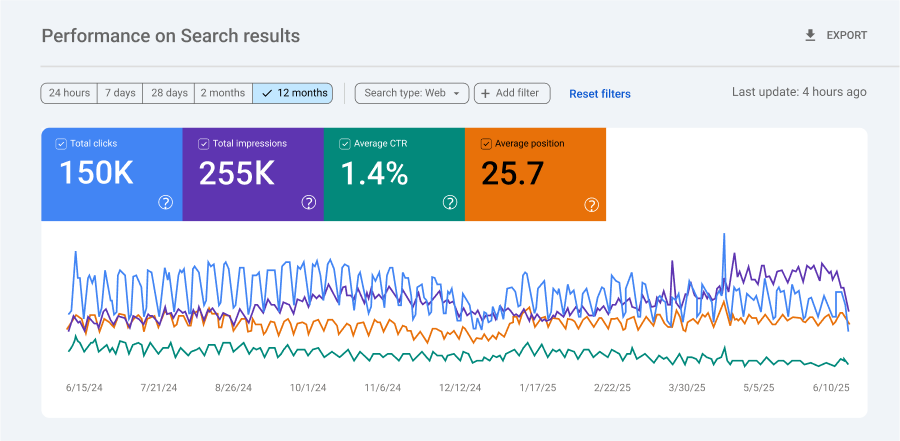
What you’ll see at the top of the Search results report:
- Total clicks. The total number of clicks on your site from the search results.
- Total impressions. How often your site appeared in search results.
- Average CTR (click-through rate). The percentage of impressions that resulted in clicks.
- Average position. The average ranking positions your pages hold for all search queries.
Why the Search results report matters
This report helps you:
- Identify high-performing keywords and pages.
- Find opportunities where pages get impressions but low clicks (low CTR).
- Spot content that ranks well but could benefit from further optimization.
- Track performance across countries, devices, and search appearances.
2. Discover report
The Discover report shows how your content performs in Google Discover, a personalized content feed that appears on the Google app and Android home screens.
Note: Unlike traditional search results, Google Discover recommends content based on users’ interests, not on their search queries.
What you’ll see in the Discover report:
- Total clicks. The number of times people clicked your content in Discover.
- Total impressions. How often your content appeared in the Discover feed.
- Average CTR (click-through rate). The percentage of impressions that resulted in clicks.
Filters and customization options in Discover:
- Date range. Choose from 24 hours, 7 days, 28 days, 3 months, or a custom range.
- Page filter. View performance data for a specific page or URL.
- Country filter. Track Discover performance by region.
- Discover appearance. This is the overall view of how your content appears in Discover, but note that AMP, rich results, and web stories aren’t listed separately.
Note: Although content types like AMP, rich results, and web stories may affect Discover performance, they are not shown as separate filters here.
Why the Discover report matters
The Discover report helps you:
- Track which pages are performing well in Google Discover.
- Understand how your content engages with users in a more visual and mobile-first environment.
- Optimize your content to increase its chances of being picked up by Google Discover.
Content with strong visuals, engaging headlines, and broad appeal tends to do better in Discover.
Indexing report
The Indexing report in Google Search Console helps you understand how well your pages are indexed by Google and if any indexing issues prevent certain pages from appearing in search results.
It includes four essential tools:
- Pages
- Videos
- Sitemaps
- Removals
Each tool provides valuable insights to ensure that your site’s content is indexed properly and that any issues are addressed swiftly.
- Pages report
The Pages report provides detailed information about how Google has indexed your website’s pages. It helps you track the status of your pages and identify any issues preventing Google from indexing them. This report is a key tool for diagnosing indexing problems and ensuring that your pages appear in search results.
What you’ll see in the Pages report:
- Indexed pages. These are the pages that Google has successfully indexed and added to its search database. You’ll want to make sure the pages you care about such as blog posts, landing pages, and product pages, are listed here.
- Excluded pages. These are pages that Google has decided not to index. The reasons could vary: pages may have a noindex tag, be marked as duplicates, or have other technical issues like blocked resources (e.g., images or JavaScript files that Google can’t crawl).
- Valid pages. Pages that are eligible for indexing and have been indexed correctly.
- Errors. Pages with issues preventing them from being indexed. This can include 404 errors (page not found), server issues (e.g., 500 errors), or any other technical issues that prevent proper indexing.
Why it matters
The Pages report is essential for monitoring your site’s indexing health. It’s important to regularly check this report to ensure your pages are being properly indexed by Google.
Note: Even blog pages (e.g., pages 1, 2, etc.) can sometimes be missed, especially if your site has a large number of pages. If some pages aren’t indexed, it’s important to identify and fix the issues preventing indexing.
Here are common issues that may prevent indexing:
- Noindex tags. If a page has a noindex tag, it will not be indexed by Google. You’ll need to remove the tag or adjust your robots.txt file to allow crawling.
- 404 errors. If a page is returning a 404 error, Google won’t be able to index it. This issue should be fixed by updating the URL or correcting any broken links.
- Server errors. Pages with server issues (like 500 errors) won’t be indexed either. These errors need to be resolved to allow proper indexing.
For more information on fixing indexing issues, you can check out this Google support guide.
What you can do:
- Regularly check the Pages report to spot and fix indexing issues. This will ensure that important pages are indexed and visible in Google Search.
- Submit pages for re-indexing. If you’ve updated or fixed a page, you can submit it for re-indexing. This helps Google crawl and index the page again, ensuring it appears in search results.
Similarly, if your site includes video content, you can monitor how well Google indexes your videos by using the Videos report.
2. Videos report
The Videos report in Google Search Console helps you understand how your video content is being indexed by Google. This is especially important for websites that rely heavily on video content, including:
- Media and news websites
- Educational platforms
- E-commerce sites with product videos
- Entertainment and streaming services
- Bloggers and content creators
- Corporate websites with marketing videos
- Travel and hospitality sites
If your site uses video to inform, engage, or convert users, monitoring this report ensures that your video content is discoverable in Google’s video search and rich results.
What you’ll see in the Videos report:
- Indexed videos. Videos that have been successfully indexed by Google and appear in video search results.
- Non-indexed videos. Videos that Google could not index, possibly due to technical issues, schema errors, or insufficient visibility.
Why it matters
Monitoring the Videos report helps you track how your video content performs in search results. If videos are not being indexed, it could affect their visibility in Google’s video search or rich results. Regular checks on this report ensure that your video content reaches its intended audience and performs well in search.
If you encounter non-indexed videos, it’s often due to issues like missing structured data, blocked resources, or poor video placement. For a full list of causes and how to fix them, refer to Google’s official guide on the Video indexing report.
3. Sitemaps Report
A sitemap is a file that lists the pages on your website, helping search engines like Google discover and crawl your content more efficiently. By submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console, you make it easier for Google to find and index your site’s important pages. This is especially useful if your site has a complex structure or many pages.
What it does
- Guides search engines. A sitemap acts as a guide for search engines, helping them understand the structure of your website. It tells Google which pages you want it to crawl and index.
- Improves crawling efficiency. It ensures that Google crawls all the important pages on your site, even if they aren’t linked to other pages.
- Helps with dynamic sites. Websites with frequently updated content or pages that are hard to discover can benefit from sitemaps, ensuring Google knows about every new or changed page.
What you’ll see in the Sitemaps report:
a. Add a new sitemap
- In this section, you can submit a new sitemap for Google to crawl. Simply enter the URL of your sitemap file (e.g., https://www.yoursite.com/sitemap.xml) and click Submit.
- Under normal circumstances, you only need to submit your sitemap once. Google can recrawl it automatically and regularly from there.
- However, you may consider re-submitting a new one following major structural changes in your site, especially those involving major URL re-structures of important / frequently updated pages and directories.
b. Submitted sitemaps
This section displays all the sitemaps you’ve submitted to Google, with the following details:
- Sitemap. The URL of the submitted sitemap.
- Type. The format of the sitemap, typically XML.
- Status. Indicates whether the sitemap was successfully processed or encountered any issues.
- Last read. The date when Google last processed the sitemap.
- Discovered pages. The number of pages Google discovered from the submitted sitemap.
- Discovered videos. If your sitemap includes videos, this will show the number of videos Google discovered from it.
Why it matters
The Sitemaps report helps you track how Google processes your sitemaps. By submitting a sitemap, you ensure that Google can easily discover and index your pages, especially on larger websites where some content may otherwise be overlooked.
Regularly monitoring this report helps you check if your sitemaps are processed correctly and if there are any issues with indexing.
Filters and options
a. Rows per page. You can adjust the number of sitemaps shown per page, allowing you to view as many or as few as you’d like (default is 10 rows per page).
b. Status filter. This filter helps you quickly check the status of your sitemaps. It lets you focus on whether your sitemaps have been successfully processed or if there are issues (e.g., file errors or invalid URLs).
c. Sitemap filters. You can filter sitemaps based on whether they are submitted, helping you track which sitemaps have been sent for crawling and which are pending.
What you can do
Regularly checking the Sitemaps report helps make sure that Google is crawling and indexing the right pages from your site. If you find any errors or issues with your sitemaps, you can correct them and resubmit your sitemap for processing.
Additionally, you can submit new sitemaps whenever you add significant updates or new pages to your site, helping Google discover your fresh content quickly.
4. Removals Report
The Removals Report in Google Search Console allows you to temporarily remove content from Google’s search results. It’s especially useful for quickly hiding outdated, sensitive, or incorrect content while you work on a more permanent solution.
These are the key features of the removals report:
- Temporary URL Removal. Temporarily hides a URL from Google Search for about six months and clears the snippet (preview text) the next time Google re-crawls the page.
- Clear Cached URL. Removes the snippet and cached version of a page but keeps the URL in search results until it’s reindexed.
- Prefix Removal. Allows you to remove all URLs that share a common prefix (e.g., a directory or category).
How to use it:
- Click “New Request” in the Removals tool.
- Enter the exact URL or prefix you want to temporarily remove.
- Choose between:
- Remove this URL only
- Remove all URLs with this prefix
- Submit the request.
Here are the sections in the Report:
- Temporary Removals. Shows active and expired temporary removal requests.
- Outdated Content. Tracks requests to remove content that no longer exists on the page.
- SafeSearch Filtering. Lets you request removal of content that may violate Google’s SafeSearch policies.
Why it matters
This tool is essential for managing content visibility in urgent situations. However, temporary removals are not permanent. For long-term removal, you should:
- Use a noindex tag,
- Block the page via robots.txt, or
- Remove the content entirely from your site.
For full details, visit Google’s official guide on the Removals tool in Search Console.
Experience report
The Experience section of Google Search Console focuses on user experience metrics that can impact how your site is perceived in search rankings. These reports help you monitor and improve aspects related to performance and accessibility.
Two critical reports here are:
- Core Web Vitals
- HTTPS
- Core Web Vitals
The Core Web Vitals report is one of the key elements that determine the user experience on your site. This report focuses on three primary factors:
a. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP). Measures how quickly the largest element on the page loads, ideally within 2.5 seconds.
b. Interaction to Next Paint (INP). Replaced First Input Delay (FID) in 2024. INP measures the responsiveness of your site to user interactions. A good INP score is under 200 milliseconds.
c. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Measures the visual stability of your site, ensuring that elements don’t shift unexpectedly as the page loads.
What you’ll see in the Core Web Vitals report
- Mobile and Desktop views. You’ll see how your site performs for both mobile and desktop users.
- Poor URLs, URLs need improvement, and good URLs. Identifies which URLs on your site are performing poorly, require improvement, or are meeting the benchmark for Core Web Vitals.
- Data segmentation. The report breaks down the performance of your pages across different devices (mobile and desktop).
Why it matters
Core Web Vitals are a ranking factor for Google, so ensuring that your pages are optimized for good user experience is critical. Google aims to improve the quality of web browsing, and pages that load quickly, respond promptly, and are visually stable are more likely to perform well in search.
For websites that heavily rely on user engagement and conversion, paying attention to these metrics is key to improving both your rankings and user retention.
2. HTTPS report
The HTTPS report in Google Search Console helps you monitor how securely your website is being served to users. Google prioritizes secure browsing experiences, and this report provides insights into how many of your site’s indexed URLs are served over HTTPS versus HTTP.
What the HTTPS report shows:
- HTTPS URLs. Displays the number of indexed URLs on your site that are served securely over HTTPS.
- Non-HTTPS URLs. Highlights any URLs still served over HTTP, which may indicate configuration issues or missed opportunities for secure delivery.
- Reasons for Non-HTTPS Indexing. The report may also show why certain URLs couldn’t be indexed via HTTPS, such as:
- Invalid or expired SSL certificates
- Canonical tags pointing to HTTP versions
- HTTPS crawling issues
Note: This report is only available for Domain properties and HTTPS URL-prefix properties.
Why it matters
Using HTTPS across your entire site is essential for:
- User trust. Visitors are more likely to engage with a site that is more secure.
- Data protection. HTTPS encrypts data in transit, protecting user information.
- SEO performance. HTTPS is a confirmed ranking signal in Google Search.
- Indexing preference. Google prefers HTTPS versions of pages when both HTTP and HTTPS are available.
The HTTPS Report allows you to quickly identify and resolve any issues preventing full HTTPS adoption, helping ensure your site is both secure and search-friendly.
Learn more about the HTTPS report in Google Search Console from Google’s official documentation.
Shopping reports
Shopping reports help eCommerce site owners effectively display their products in the Google Shopping tab. These reports allow you to monitor the visibility and performance of your product listings, identify potential issues, and optimize your product data for better results.
To access this data, simply link your Google Merchant Center with Google Search Console.
Shopping Reports in GSC
Depending on the structured data Google finds on your website, you may see one or more of the following reports:
- Product Snippets. Available if Google detects Product Snippet structured data on your site. This includes pages with product reviews or aggregated product details from multiple sources.
- Merchant Listings. Shown when Google identifies Merchant Listing structured data on your site. It relates to pages where products are sold.
- Shopping Tab Listings. If your products are eligible to appear in the Google Shopping tab, this report will show the status of your listings, or provide instructions on how to make them eligible.
Enhancements reports
Structured data helps your content stand out in Google Search results by enabling rich results—enhanced listings that include additional visual or interactive elements. These features can significantly improve your click-through rates. If your site lacks properly implemented structured data, you may miss out on valuable search visibility and traffic.
In Google Search Console, the Enhancements section provides detailed reports for each type of rich result that Google detects on your site. These reports highlight:
- Which structured data types are present
- Any issues or errors found during parsing
- Opportunities to improve how your content appears in search
Use these reports to identify and fix problems that may prevent Google from correctly interpreting and displaying your content as rich results.
Rich Result Types in GSC
Google Search Console supports enhancement reports for a variety of structured data types. Some of the most common include:
- Breadcrumbs
- Courses
- Education Q&A
- Events
- FAQs
- Hotels
- Image metadata
- Job postings
- Merchant listings
- Products
- Profiles
- Q&A pages
- Recipes
- Review snippets
- Special announcements
- Vacation rentals
- Videos
- Vehicle listings
- Learning videos
- Math solvers
- Practice problems
- Fact checks
- Datasets
- Discussion forums
- Subscribed content
Note: GSC only shows reports for rich result types that are both supported by Google and detected on your site. For a full and updated list, refer to Google’s official documentation on Search Gallery.
Security and manual actions reports
The Security and Manual Actions section of Google Search Console provides critical information about your website’s security and compliance with Google’s guidelines. It includes two main reports: Manual Actions and Security Issues.
These reports help you monitor and fix any security vulnerabilities and penalties imposed by Google, ensuring that your site remains trustworthy and compliant.
- Manual actions report
The Manual Actions report shows whether Google has applied any penalties to your site for violating its Search Essentials (formerly Webmaster Guidelines). These actions are manually applied by human reviewers when they detect issues such as:
- Spammy or deceptive content
- Unnatural backlinks
- Cloaking or sneaky redirects
- Structured data abuse
What you’ll see in the Manual Actions report:
- Manual Action Types. Specific violations like “Unnatural links to your site” or “Spammy structured data.”
- Status. Indicates whether the issue is “Pending,” “Resolved,” or “Not yet resolved.”
- Details. A description of the issue, affected URLs, and steps to fix it.
Why it matters
Manual actions can significantly reduce your site’s visibility in Google Search. To recover, you must fix the issue and submit a Reconsideration Request through Search Console. Google will then re-evaluate your site and may lift the penalty if the issue is resolved.
2. Security issues report
The Security Issues report alerts you to any malicious activity detected on your site, such as:
- Malware
- Phishing attacks
- Hacked content
- Unwanted software
Google flags these issues to protect users and may display warnings in search results or browsers if your site is compromised.
What you’ll see in the Security Issues report:
- Detected Issues. Lists the type of threat (e.g., malware, phishing).
- Date of Detection. When was the issue first identified.
- Detailed Information. Descriptions of the threat and sample affected URLs.
Why it matters
Security issues can damage your site’s reputation, reduce traffic, and trigger browser warnings that deter users. Promptly resolving these problems is critical to restoring trust and maintaining your search presence.
Explore Google’s official guide for a deeper understanding of the Security & Manual Actions Reports.
Other tools and options
At the bottom of the Google Search Console sidebar, you’ll find tools that support your overall setup and user experience. These aren’t core SEO reports but still play an important role in managing your property and accessing key information.
- Links report
The Links report shows how your site is connected both internally and externally:
- External links. See which websites are linking to your content. This helps you identify valuable backlinks and assess your site’s authority.
- Internal links. Understand how your own pages are linked together, which can influence how link equity flows and how Google crawls your site.
This report is useful for spotting SEO opportunities, auditing link structures, and ensuring your most important pages are well-supported
Learn more about the Links report here.
2. Settings
The Settings panel in Google Search Console is where you manage technical configurations and property access. While it doesn’t affect rankings directly, it supports important administrative tasks that help keep your account organized.
What you can do in the Settings panel:
- Manage ownership verification. Add or remove verification methods to confirm site ownership.
- Adjust user permissions. Control who can access your property and what actions they can perform.
- Configure crawling preferences. Request a reduced crawl rate if Googlebot is causing server strain.
- Switch between property types. Toggle between domain-level and URL-prefix properties.
- Use the domain change tool. Inform Google when moving to a new domain to help preserve indexing signals.
Understanding account roles
Each user is assigned a role that determines their level of access:
- Owner. Full control over settings, users, and data. There are two types of owners in GSC:
- Verified owner. Gained access through site verification.
- Delegated owner. Granted ownership by a verified owner.
- Full user. Can view all data and perform key tasks like submitting sitemaps.
- Restricted user. Has limited, view-only access.
- Associate. Can connect GSC to other Google services but cannot view data within the interface.
Learn more about managing users and permissions in Google Search Console.
3. Submit feedback
Use this option to send feedback directly to Google. Whether you’ve encountered a bug or have suggestions for improvement, this tool helps you communicate with the Search Console team.
4. About Search Console
This section provides general information about your current version of Search Console and includes links to:
- Official documentation
- Help resources
- Support channels
It’s a helpful starting point for troubleshooting or learning more about the platform.
These sections don’t influence search performance directly. However, they help keep your account organized, secure, and easier to manage — especially if multiple people are working on the site.
How to use Google Search Console to boost your SEO performance
GSC is not just a tool for monitoring your website’s search performance; it’s a powerful asset for actively improving SEO.
Here are different ways in which you can use GSC to enhance your SEO efforts:
1. Identify high-performing pages → Optimize for conversions
High-performing pages in GSC are an excellent starting point for further optimization. You can use GSC data to identify which pages are attracting the most clicks and impressions.
Once you spot these pages, focus on improving their conversion potential by refining CTAs, enhancing user experience, or adding more targeted content. Optimizing these pages based on their existing success will help you drive even better results.
2. Spot declining pages → Refresh/update content
Pages that once ranked well but have started to decline need attention. GSC can help you track when a page’s performance starts to dip, whether in terms of clicks, impressions, or CTR.
This information is important for identifying pages that need refreshing. Updating content, adding new information, or re-optimizing targeted keywords can help revive these pages and bring them back into the competitive search rankings.
3. Discover new search queries → Content ideation
With GSC, you can uncover search queries that are bringing traffic to your site, even if they weren’t part of your original content strategy. Use this data to identify new keyword opportunities and generate content ideas (or update existing content).
For example, if you notice an unexpected but relevant search term, you can create a blog post or landing page to target that term more effectively. This increases your site’s overall visibility.
4. Monitor indexing issues → Resolve technical SEO gaps
Indexing issues can prevent your valuable pages from appearing in search results. GSC’s Coverage report provides insight into which pages are indexed and which are facing errors.
Regularly monitoring this section helps you address issues like 404 errors, server problems, or content being excluded due to noindex tags. Fixing these technical issues ensures that important pages are included in the search index.
- Re-submit important pages → Faster indexing after updates
After making updates or resolving errors, use the URL Inspection Tool in GSC to request re-indexing. This is especially useful if you’ve added new content, fixed technical issues, or updated an existing page.
Submitting the page for re-indexing ensures that Google reflects the latest version of your page in search results as quickly as possible.
- Pair GSC with GA4 for behavior-based prioritization
To enhance your SEO decisions, pair GSC with GA4. While GSC provides search data, GA4 tracks user behavior on your site. Integrating both tools allows you to prioritize optimization efforts based on search performance and user engagement.
For instance, you can identify pages that rank well but underperform in user engagement, enabling you to target areas for improvement.
Why GSC is your SEO MVP
Google Search Console provides invaluable insights into how your site performs in search results, helping you identify strengths and weaknesses. Regularly monitoring GSC ensures that your site stays visible, healthy, and optimized for SEO success. By using this tool, you’ll be able to track performance, resolve issues, and make data-driven decisions to boost your rankings.
Network Solutions offers the tools and support you need to optimize your site’s performance. With reliable hosting services and expert SEO solutions, we can help you leverage GSC to its fullest potential and grow your online presence.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Yes. GSC shows how your site performs in Google search, even if you don’t run ads. It helps you track performance and improve your visibility online.
It means your page has been deliberately blocked from indexing. To fix it, remove the noindex tag or adjust your robots.txt file to allow Google to crawl the page.
Indirectly. GSC helps you discover what needs improvement, whether it’s optimizing a high-ranking page or fixing indexing issues. You can use that information to update content, that can lead to better rankings over time.
There are several reasons: crawl budget limitations, poor page structure, improper canonical tags, or low-quality content. Use the Pages report in GSC to identify and resolve these issues.
“Indexed” means your page appears in search results, while “Submitted URL not found” means GSC couldn’t access the URL you submitted, which could be due to server issues or a broken link.
Different tools, different scopes. Even the ‘Search Console’ section in GA4’s Acquisition module often does not report the same exact numbers (although they are close enough for the difference to matter). It’s important to understand that GSC tracks organic search data from Google only (excluding traffic from Bing, DuckDuckGo etc), while GA4 reports all traffic types, including paid and social media.




