Key takeaways:
- Rate limits are set on websites to prevent multiple requests at a specific timeframe.
- Once this limit is reached, the website server will issue an HTTP error 429, which signifies that there are too many requests.
- The error is caused by multiple factors: bot attacks, corrupted cache, misconfigured APIs, etc.
Have you ever encountered a frustrating “Too many requests” error message? It’s typically caused by HTTP error 429. This request error disrupts the user experience and indicates server overload or abuse.
Resolving errors like this is important to maintain excellent website performance and user experience. But how do you do it? Let’s tackle the HTTP 429 error, what causes it, and how to fix it for both users and website owners here.
What is HTTP error 429?
An HTTP error 429 means there are too many requests to a server within a specific time frame. This triggers the server’s rate limit, which helps stop malicious bot activities and distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
Here’s what it typically looks like for Microsoft Edge browsers:

There are various 429 error displays, and it varies per browser and device. Here are a few you might encounter:
- 429 Too Many Requests (Google Chrome)
- HTTP code 429
- HTTP error code 429
- HTTP status code 429
- 429 Error
- HTTP 429
- Response code 429
- 429 error: you are being rate limited (WordPress)
- Error 429 (Too Many Requests)
- Something went wrong. Please try again. (mobile devices)
- There was a problem with the server 429
- Problem with the server 429
What is rate limiting?
Rate limiting is a strategy for managing network traffic and controlling the frequency of requests made to a server or API. It involves setting a cap on how many times a user, IP address, application, or other entity can perform a specific action within a defined timeframe.
Rate limiting usually involves:
- Identifying the requester (IP address, session ID, etc)
- Defining a time window (e.g. users are only allowed 5 requests per minute)
This is where rate limiting directly connects to the HTTP 429 error. When a server’s rate-limiting mechanism detects that a client has sent too many requests within the allowed timeframe, it responds by issuing an HTTP 429 “Too Many Requests” status code.
What causes the HTTP 429 error?
As its name suggests, the “Too Many Requests” error occurs when the server detects numerous spammy requests. But there are other possible causes that might affect your server’s resource limits:
- Brute-force login attempts or attacks
- Misconfigured APIs or installed plugins
- Shared hosting resource limits
Let’s discuss these causes deeper:
Brute-force login attempts or attacks
Brute-force login attempts are a systematic attack in which login credentials, encryption keys, and other sensitive information are guessed to access data, accounts, or systems.
Cybercriminals use tools like bots and scrapers to initiate brute-force attacks. These attacks use high-volume requests to overwhelm their target server. In response, the server issues an HTTP 429 “Too Many Requests” error to the attacker’s source to effectively block the attacks.
Misconfigured APIs or installed plugins
Your browser’s extensions or content management system’s (CMS) active plugins frequently make requests that could push a website’s rate limits. A few examples of these include:
- Improperly configured chatbots or live chat plugins that constantly refresh every second
- Automated security scanners that are performing high-volume checks for vulnerabilities
- Improperly cached social media feeds that constantly use a frequent external API to retrieve updated posts
Shared hosting resource limits
A website’s hosting type also affects its performance. For instance, websites with shared hosting are more likely to encounter the “Too many requests” error because of limited resources. This limitation stems from resource allocations.
Shared hosting often has a fixed amount of bandwidth for websites. If there’s a sudden surge in traffic on one site, it will exhaust all of its allocated share and make it difficult to balance with the other websites.
Signs that the shared hosting is causing the HTTP error 429 include:
- Slow website performance
- Errors during peak hours
- Other sites on the same server are experiencing the same issues
How HTTP Error 429 affects your website and SEO
Getting a “Too many requests” error goes beyond annoying site visitors: it also impacts your site’s overall search engine optimization (SEO) performance. If the error persists, it could:
- Impact crawl budget and Googlebot. A 429 error signals Googlebot that your website’s server is unstable or overloaded. With this information, it will slow down or stop crawling your site and prevent it from indexing new content.
- Missed indexing and ranking delays. The decreased crawl budget leads to your website not appearing in search results for new content or delays updates to existing content’s ranking. Google prioritizes stable, accessible websites, and having persistent 429 errors tell Google that your site is unreliable.
- Poor user experience. A 429 error creates immediate frustration for users trying to log in or checkout items on your website. This lessens user trust and impacts your brand’s credibility. It also causes lost revenue for eCommerce sites.
How to fix HTTP 429 (for users)
Are you receiving “Too many requests” errors consistently? Here are a few ways you can fix it on your end:
- Wait and retry later
- Clear browser cache
- Flush DNS cache
- Try a different network or IP
Now, let’s discuss the solutions in full:
Wait and retry later
Before proceeding to the other technical steps, it’s best to wait it out first to see if the issue will be resolved after a few minutes. The 429 error often indicates a temporary server overload or a rate limit reset, which means normal service can resume after a short period.
Clear browser cache
Sometimes, the HTTP 429 error is caused by a corrupted or outdated cache in your browser. This option is typically found in the browsing history data section of your browser’s privacy and security settings.
For Microsoft Edge
- Click the three dots on the top right corner of your screen
- Scroll down until you see Settings
- You have the option to use the search bar and look for the cache
- Select the Clear browsing data option from the search
- Click Choose what to clear next to the Clear browsing data now
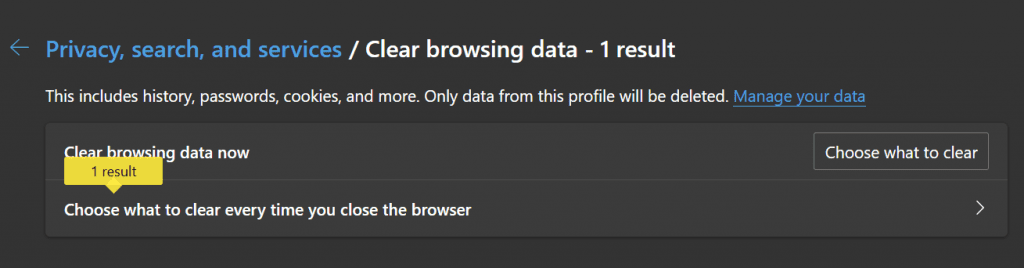
6. Check the box next to Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files
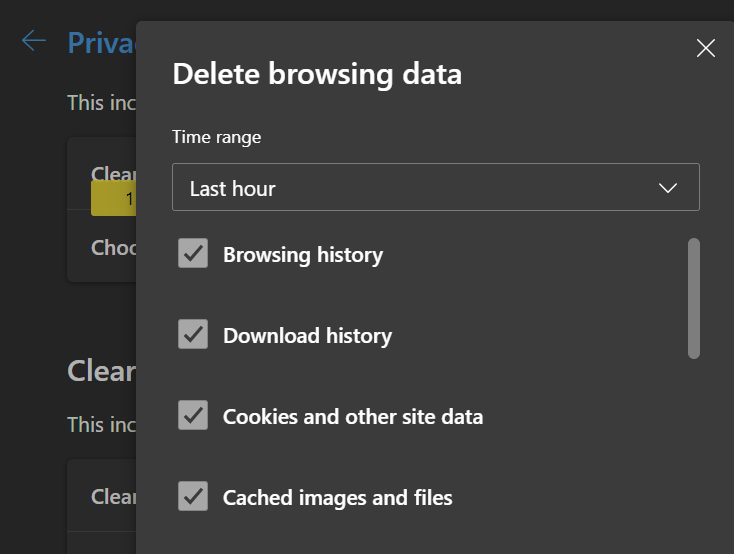
For Google Chrome:
- Click on the three dots in the top right corner of your screen
- Choose Delete browsing data
- Pick your preferred time range (Last hour or All time)
- Click the check box for the Cached images and files
- Click Delete data
For Safari:
- Go to Settings > Apps > Safari
- Click Clear History and Website Data
- Select the clear timeframe you prefer (Last our, Today, Today and yesterday, or All history)
Flush DNS cache
If clearing your browser cache doesn’t work, also clear your DNS cache. Your computer stores DNS records of every web page you visit, including the domain name and IP address, to make pages load faster on the next visit. These records can get corrupted and cause connection issues.
You can resolve this by flushing the DNS cache on your computer.
If you’re using Windows, follow these steps:
- Click the Start button and enter “CMD” into the search bar
- Right-click the Command Prompt and choose to Run as administrator
- Enter this code into the DNS command: Ipconfig /flushdns
- And that’s it. You will see a confirmation in the Command Prompt after.
For macOs
- Open Terminal: Go to Applications > Utilities > Terminal.
- Execute the command (varies by macOS version):
| OS | Command |
| Big Sur Monterey Ventura Sonoma Sequoia | sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder |
| El Capitan Sierra High Sierra Mojave Catalina | sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder |
| Yosemite | sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches |
| Lion Mountain Lion Mavericks | sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder |
| Snow Leopard | sudo dscacheutil -flushcache |
| Leopard | sudo lookupd -flushcache |
3. Enter your password if the Terminal asks for authorization. There is usually no confirmation message for macOS.
Try a different network or IP
If you still encounter HTTP 429 errors after clearing your browser and DNS cache, the problem might be your network’s IP address. The server’s rate limiting often tracks requests based on the client’s IP address, and if yours has exceeded the allowed request threshold, the server will block incoming requests from your IP address.
You can try to:
- Switch to a mobile data connection
- Use a different Wi-Fi connection
- Restart your router or modem
- Use a virtual private network (VPN)
- Use a proxy server
How to fix HTTP 429 (for website owners)
If the “Too many requests” error persists for multiple users, the issue might not be on the client’s end and could be within your website. Here are the steps that will resolve these performance issues:
- Monitor server logs and headers
- Upgrade your hosting plan
- Disable and audit plugins/themes
- Limit log in attempts
- Batch or cache API requests
- Use exponential backoff
- Switch to OAuth for third-party logins
- Contact your hosting provider
Here are the steps in detail:
1. Monitor server logs and headers
Check your website’s logs for patterns of excessive requests. Look for specific IP addresses, user agents, or endpoints that trigger the HTTP 429 error. Also, pay attention to the Retry-After header, which usually indicates the recommended time that the client should wait before making another request.
It usually looks like this:
import time
import requests
response = requests.get(“https://api.example.com/data“)
if response.status_code == 429:
retry_after = int(response.headers.get(“Retry-After”, 60))
print(f”Rate limit exceeded. Retrying after {retry_after} seconds.”)
time.sleep(retry_after)
response = requests.get(“https://api.example.com/data“)
2. Upgrade your hosting plan
As mentioned above, one of the main causes of the HTTP 429 error is server resource limits. Check if your current hosting plan meet your current website traffic requirements. If your server frequently hits its CPU, RAM, or bandwidth limits, upgrade your plans or switch to a new hosting provider.
3. Disable or audit plugins/themes (WordPress)
Poorly coded or resource-intensive WordPress plugins generate excessive database queries that cause 429 errors. To identify which plugin is causing the error, follow these steps:
- Go to your WordPress admin area > Plugins > Installed plugins.
- Choose the Deactivate option under the plugin you’re suspicious of.
- Open a browser in incognito mode and access your website to see if the HTTP 429 error message still appears.
- If the 429 error still appears, repeat the steps for all your active plugins until you find the trigger.
In addition to plugins, your website’s active theme could also be a culprit. You can fix this by:
- Switching to a default WordPress theme. But before doing so, make sure to back up your website’s data. Activate a default theme like “Twenty Twenty-Four” or “Twenty Twenty-Three” via Appearance > Themes. Check your site in incognito mode for the 429 error.
- Auditing the theme code. If a custom theme causes the issue, review its code. Look for inefficient loops, repeated external API calls, or unnecessary scripts that overwhelm the server.
In case you can’t access your WordPress admin area, use phpMyAdmin or a file transfer protocol (FTP) client to manage plugins and themes.
4. Limit login attempts
To prevent brute force attacks, integrate CAPTCHAs into your login pages. CAPTCHAs involve visual or auditory puzzles that are easily answerable by humans but difficult for bots. This helps slow down automated attempts and blocks malicious request frequency that triggers the 429 Too Many Requests error.
5. Batch or cache API requests
If your website frequently uses external APIs, optimize these by setting a given number of allowable requests. This reduces request frequency that could overwhelm server resource limits. Implement caching for frequently used API data and store it temporarily on your server to avoid having to re-fetch the same information repeatedly.
6. Use exponential backoff
Implement an exponential backoff strategy if your website or users interact with an API that causes 429 Too Many Requests errors. This involves progressively increasing the wait time between retries after making consecutive failed request attempts.
7. Switch to OAuth for third-party logins
For websites that use specific third-party services for their login pages (e.g., Sign in with Facebook or Login with Google Account), use OAuth 2.0. It’s an authorization framework that gives consent to applications on your behalf to access information or perform actions without sharing your actual login credentials.
For example, let’s say your eCommerce website allows users to log in using their existing Google Account. When they click “Sign in with Google,” they will be redirected to Google’s official login page or a pop-up.
The user will enter their details directly on Google’s domain and not on your website. Once successfully logged in, Google will send a unique and temporary access token to your website. Since your eCommerce site is not constantly sending direct login attempts, you will reduce the likelihood of triggering a 429 Too Many Requests error.
8. Contact your hosting provider
If all else fails and you’ve tried every method above, contact your hosting provider to report the persistent errors. They possess the tools and access to diagnose server-side issues beyond your control.
Make sure to provide them with these additional details:
- Timestamps of when the error code appears
- URLs of affected web pages or API endpoints
- Patterns (e.g., errors are appearing during peak traffic times, geographic locations of users that commonly experience it, or certain actions that trigger it)
- Screenshots of the error message
How to avoid HTTP error 429
Like other error codes, the HTTP 429 error can be avoided if you take the appropriate precautions as a user and website owner.
For users
As an end-user, preventing 429 errors is about being mindful of browsing and understanding that websites have limits. Make sure to:
- Avoid rapid refreshing or clicking on links too quickly. If you’re using an automated tool or browser extension that sends many requests, pause or disable it.
- Make it a habit to clear your browser’s cache and cookies to get rid of outdated and corrupted cached data.
- Configure your browser extensions to avoid unintentionally sending excessive requests to websites. Always review installed extensions. If you suspect one causes issues, temporarily deactivate it to see if it makes an impact.
For website owners
Your user’s actions are just one part of the equation. As a website owner, you are also responsible for keeping your website free from 429 “Too many requests” errors. So, ensure that you:
- Set different request limits based on user type (e.g., higher for authenticated users, lower for guests, distinct for API keys). Also, set rate limits to specific and high-resource endpoints such as login pages/forms and search functions rather than applying them to your whole site.
- Implement temporary account locking after a specific number of login attempts. For example, users will have to wait for a specific minute after three to five failed attempts to make them stop sending requests.
- Review and optimize your website’s codebase. Look for inefficient queries, redundant operations, or memory leaks that can degrade performance.
- Employ content delivery networks (CDNs) so when a user requests content, the CDN serves it from the nearest server, lessening the load on your main server.
- Ensure strict anti-bot and security measures are in effect alongside basic rate limiting and login attempt controls. This includes deploying a web application firewall and honeypots.
Prevent HTTP Error 429 by upgrading to a better hosting provider
When resolving the 429 “Too many requests” error, keep in mind that there could be multiple causes that go beyond the client’s side; it could be from your end, too. Proactive measures from both sides are important for ensuring a stable and accessible online experience.
Users must manage their request frequency and browser settings. Website owners, on the other hand, need to implement effective rate limits, optimize performance, deploy security measures, and upgrade their hosting plans. At Network Solutions, we offer flexible and reliable hosting plans fit for personal use and businesses. Contact us to upscale your website’s performance.
Frequently asked questions
Fixing a “Too many requests” error mostly involves users reducing their request frequency and waiting and retrying after a short period, while website owners need to implement rate limiting, address the server resource limits, and auditing problematic plugins/codes.
For users, they should practice mindful browsing, reduce request frequency, and keep their browser’s data and extension clean. Meanwhile, website owners need to deploy anti-bot measures, optimize third-party integrations, and implement smart rate limiting.
No, HTTP error 429 is generally temporary. The error typically resolves itself after the defined waiting period (often indicated by a Retry-After header) expires. But getting repeated excessive requests can lead to longer temporary blocks. In some cases, it could lead to permanent IP bans.
Not directly. The error is not a definitive proof of malware, but it can cause it.
“Too many” is relative and depends entirely on the server’s specific rate limit configuration. There is no universal standard.
429 “Too many requests” error negatively impact:
User experience
Sales and revenue
Your website’s SEO performance
Your brand’s credibility and reputation




