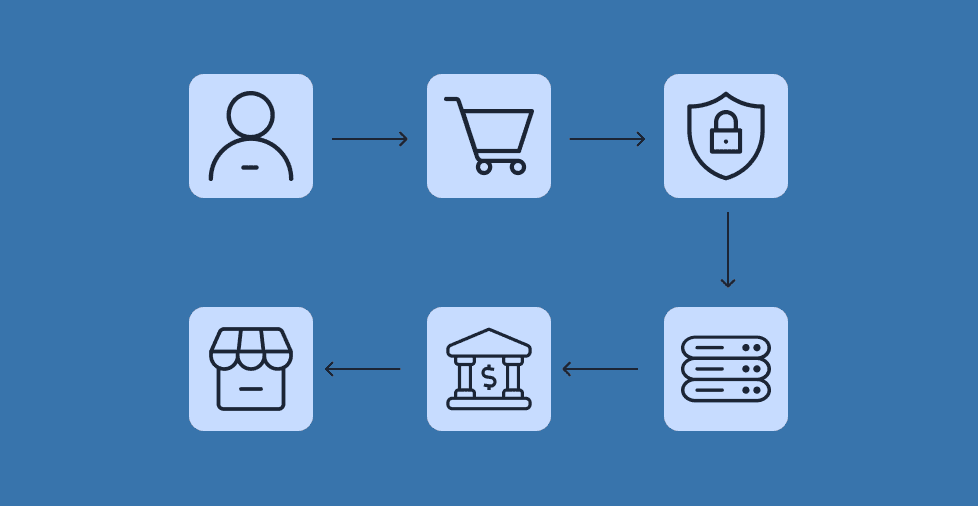
Key takeaways:
- A payment gateway encrypts a customer’s payment information into a token that cannot be traced back to their account. This keeps sensitive data safe from hackers.
- Gateways do more than just encrypt. They also help authorize transactions, perform fraud checks, and update customers on the status of their transaction.
- To prevent hackers from connecting a transaction to a customer’s account, payment gateways do not communicate with banks. Instead, payment processors serve as the courier, handling that interaction separately.
Now, only 16% of payments are done by cash. This means that modern businesses thrive on electronic payment methods.
These digital payment methods are popular because they’re fast, convenient, and easy to keep track of. However, setting this up is a little more nuanced than it might seem. For a business to process electronic payments, it needs to account for security risks and navigate an overwhelming number of payment options.
Payment gateways offer a way to manage these complexities. But what is a payment gateway exactly, and how can it help your business securely manage transaction data?
Stick with us as we explore the ins and outs of payment gateways and how they make online transactions safer and smoother for everyone.
What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway is the technology or software that acts as an intermediary between a customer, a business, and their financial institutions.
Its primary function is to encrypt customer data to prevent fraud and data breaches during payment processing. Think of it like a mailing envelope: it keeps the contents hidden and secure, using a unique code or tracking system to make sure the payment reaches the right destination safely.
Benefits of using a payment gateway
Apart from data encryption payment gateways also streamline the entire transaction process for both merchants and customers. Here is how it improves payment processing:
- Prevents fraudulent transactions
- Streamlines the payment process
- Keeps businesses compliant with security measures
- Enables global reach and multiple payment methods
- Provides valuable data and analytics
We’ll explain how a payment gateway can do all these in the sections below.
Prevents fraudulent transactions
A payment gateway automatically encrypts sensitive payment information so that only authorized parties can access it. This process provides a strong line of defense against fraud.
Streamlines the payment process
The payment gateway automates the entire transaction flow from authorization to settlement, ensuring a fast and smooth experience for both the merchant and the customer. It also handles all the behind-the-scenes communication for things like refunds and financial documentation, which means merchants don’t have to deal with each bank’s individual systems. This automation simplifies complex processes and saves the business a significant amount of time.
Keeps businesses compliant with payment security measures
A payment gateway’s encryption and tokenization systems are designed to meet standards set by the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Businesses that fail to meet these standards are often fined thousands of dollars, so the gateway’s role in helping you stay compliant is a key benefit.
Enables global reach and multiple payment methods
A payment gateway helps businesses expand their market and accept a wide range of alternative payment methods, such as digital wallets (e.g. Apple Pay, Google Pay). To do this, merchants should configure their payment gateway to set which currencies to accept and how to present them to consumers for a smoother checkout experience.
Provides valuable data and analytics
Because the payment gateway acts as a central hub for all transactions, it provides businesses with a single source of truth for their sales data. This data can be used for financial reporting, reconciliation, and gaining insights into customer purchasing habits, which helps businesses make more informed decisions about their marketing and growth strategies.
How do payment gateways work?
To understand how payment gateways work, we’ll have to look at how they function within the transaction process. This is what happens in a transaction:
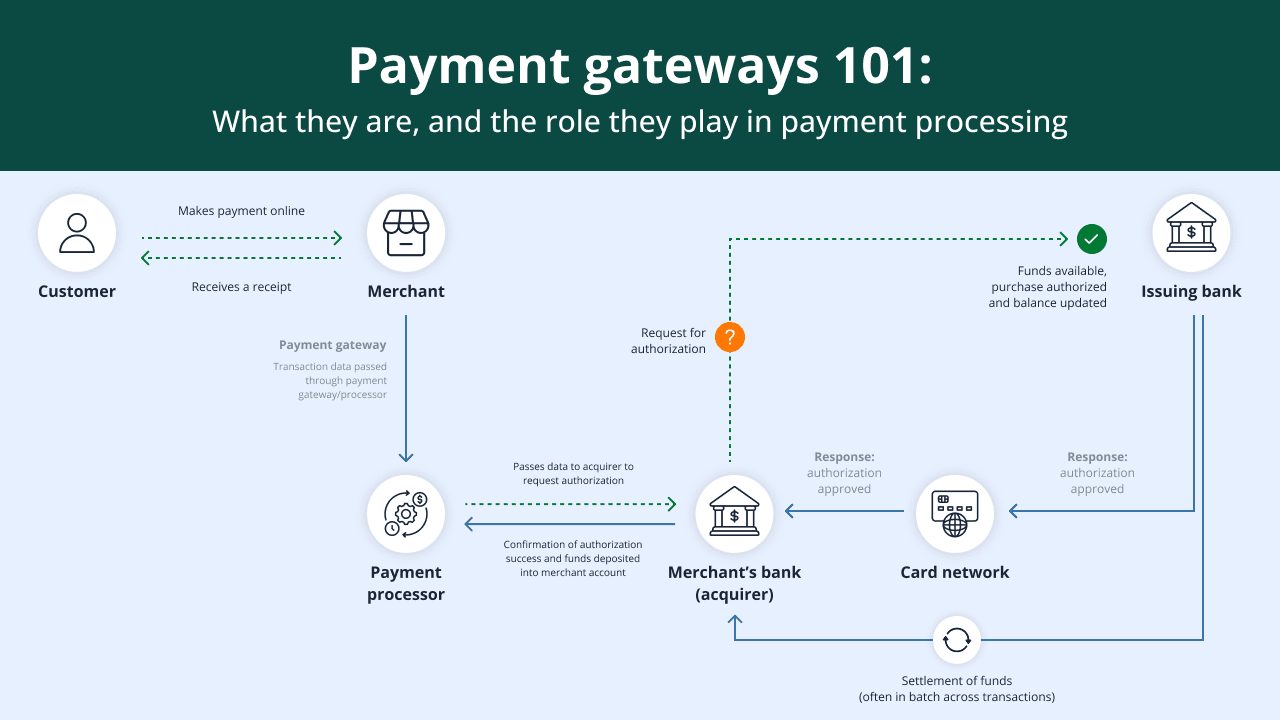
- Customers submit their payment information
- The payment gateway secures the payment details
- Customer information is authenticated
- Payment processing begins
- The payment gateway informs customers of the transaction status.
Read on to see where a payment gateway fits into the process.
1. Customers submit their payment information
This is when the customer enters their payment information into an online form or swipes their card in a point-of-sale (POS) machine.
2. The payment gateway secures the payment details
After a customer clicks Submit Payment, the payment gateway encrypts and tokenizes the data to ensure no one else can access it.
It first uses encryption protocols like a website’s Secure Socket Layer (SSL) to scramble the customer’s card details into an unreadable format. The payment gateway then proceeds to create a unique, randomized alphanumeric code (token) to represent the sensitive card number. The token has no monetary value, so the data a merchant has on file is useless to a fraudster.
Once all these safety precautions are completed, preliminary authentication can be performed.
3. Customer information is authenticated
The payment gateway can’t access bank details, but it does initiate preliminary authentication and fraud checks. It uses 3D Secure 2 (3DS2) to check for online payments to verify the cardholder’s identity.
This process can be frictionless for low-risk transactions but may involve an additional step for higher-risk ones, such as:
- Asking for a one-time pin (OTP)
- Asking for email verification
- Making customers do a biometrics confirmation (finger/face)
- Confirming device information (if accounts are registered on other devices)
The gateway also collects the billing address and the Card Verification Value (CVV) code from the customer. It passes this data, along with the results of the 3DS2 check and the encrypted payment information, to the payment processor.
Note: This applies to both in-store and online payments.
4. Payment processing begins
The payment gateway turns over the encrypted data along with an authorization request to the payment processor. The processor forwards these to the customer’s issuing bank.
The bank then decrypts the data and validates the information. This check includes:
- The customer’s previous transactions.
- A verification of available funds to cover the transaction amount.
- A check of the card’s status (e.g., whether it is expired or reported stolen).
- Its own internal fraud detection rules.
Based on these checks, the bank sends back an authorization code to the payment processor to confirm that the transaction is approved or denied. The payment processor also updates the acquiring bank of the transaction details and status.
5. The payment gateway informs customers of the transaction status
The payment processor turns over the transaction status to the payment gateway, which then passes it on to the customer. If the transaction failed, the payment gateway sends customers a prompt to pick out an alternative payment method.
The gateway also records the entire transaction in its system. This data can be pulled for credit reports, refunds, and any other necessary financial documentation.
Payment gateways vs. payment processors
Payment gateways and processors both help connect your business to your customers’ financial institutions. They are often confused because they work so closely together.
Here is how they work together:
As the first point of contact, the payment gateway secures your customer’s payment information and sends it to the payment processor. The processor then serves as the bridge to financial institutions by sending that information through a secure channel to the customer’s bank for approval.
When you look at it closely, you’ll see the payment gateway doesn’t have any direct contact with any financial institutions at all. They’re simply messengers with limited understanding of the financial process.
This security measure ensures that if fraudsters gain access to their data, it cannot be used to trace back to a customer’s actual financial information.
Types of payment gateways
It’s important to pick the right payment gateway from the start as it directly affects customers’ confidence in making a purchase. While it may be tempting to test the waters, changing your gateways will be confusing and sketchy.
With that said, it’s important to choose a payment gateway that works best for you and your brand.
Here are the 4 types of gateways to choose from:
- Hosted payment gateways
- API-hosted payment gateways
- Self hosted payment gateways
- Local bank integrations
We’ve covered each of these payment gateway types in more detail below.
Hosted payment gateways
With this setup, your customer is sent to a separate, secure page to pay. This page is run by your payment gateway provider.
The provider collects the payment info directly, so none of it is processed or stored on your site. This makes it a simple and secure option.
However, some customers might be hesitant to leave your site to pay. To help with this, it’s a good idea to use common and trusted providers like PayPal and Stripe. When people see a familiar name, they feel more comfortable giving out their information.
API-hosted payment gateways (on-site payments)
Application programming interface (API) hosted gateways take payments on your own site. It might look like you’re handling the payment, but an outside provider is doing the work through an API.
Your customer never has to leave your website during checkout. This builds brand trust and often leads to more completed sales. The customer’s payment info still goes straight to the provider’s secure servers, so you get a professional look combined with strong security.
Self-hosted payment gateways
If you want full control over the checkout experience, you can host your own payment gateway. This means you collect, store, and process all customer payment information on your own servers. This gives you a lot of flexibility and can lead to lower transaction costs.
However, this approach comes with a lot of responsibility. A payment gateway’s job includes encrypting transactions and protecting user data. Managing this along with meeting complex PCI security standards for online payments, can be too much for many businesses to handle alone.
Local bank integrations
These gateways connect your website directly to a specific bank to process payments. They are often used by businesses that operate in a limited area or have a good relationship with a local bank. This can be a cost-effective option for businesses that don’t sell products or services nationwide.
Where to get payment gateway services
There are three many ways to secure a payment gateway, including:
- eCommerce website builders
- Bank-provided payment gateway
- Payment aggregators
eCommerce website builders
Many eCommerce website builders offer a built-in payment solution. This is the simplest option, as the gateway is enabled by default. To use this, you’ll need to sign up for an eCommerce website builder plan.
Bank-provided payment gateway
You can also get payment gateway services by signing up for a business bank account. This is a separate payment gateway that connects to your own merchant account.
This option offers more control and the ability to shop for the best rates for each service. However, it requires a more complex setup using an API to connect the gateway to your eCommerce platform.
Payment aggregators
These are third-party providers (e.g. Stripe and PayPal) that offer easy-to-install plugins for most major eCommerce platforms. This option balances flexibility with a straightforward setup process.
Some business owners prefer this setup because payment aggregators provide a full-package service and give them the flexibility to switch between different hosting platforms without changing their payment gateway.
Aggregators often charge less than a traditional merchant account, but their flat-rate pricing can be more expensive for high-volume businesses. They also offer less control over the user experience and can be subject to fund holds or even account freezes.
What to look for in a payment gateway?
Each payment gateway provider has its own unique advantages, but it’s crucial to look into each one specifically. That’s because every provider has its own set of limitations, guidelines, and other important factors to consider.
Here are a few things to look at:
- Costs. Most third-party providers will charge setup fees, monthly fees, and per-transaction fees. While these are usually mentioned upfront, you need to look for other hidden charges like chargeback fees, currency exchange fees, and any monthly minimums.
- Supports different payment methods and currencies. The gateway should support your customers’ preferred payment methods, including major credit cards, digital wallets, and different currencies. If you plan to expand globally, you won’t need to reconfigure your entire payment system.
- User Experience (UX). The gateway should provide a smooth and simple checkout process. A clunky or confusing checkout can lead to cart abandonment and lost sales. Look for a gateway that offers a smooth, branded experience on your site without unnecessary redirects.
- Support and customer service. Look for a provider with reliable, accessible support to prevent costly downtime.
- Integration Capabilities. Make sure your payment gateway can work with your existing eCommerce platform, accounting software and analytics tools. If not check if you can use an APIs or easy-to-install plugins instead.
If you’re looking to create an eCommerce site, the easiest choice would be to go with the default payment gateway provided by your platform. This approach ensures your customers’ payment details are kept within your builder’s system.
Build trust with a secure checkout experience
Now that you know what a payment gateway is, how it works, and what to look for when finding one, you can feel confident in processing payments for your customers.
If you’re ready to build your online store, our eCommerce website builder has all you need for a safe, secure, and simple checkout process.
Our eCommerce website package includes an online payment gateway, a free one-month SSL certificate, and social store integration to help you expand your selling capabilities. Plus, you’ll have access to a 24/7 support team to assist you with your payment needs.
Get started with your eCommerce store today and give your customers the secure shopping experience they deserve.
Frequently asked questions
There is no single “best” type. The ideal choice depends on your business’s needs. However, API-hosted gateway is often the best choice for building trust since it lets customers complete their purchase without ever leaving your website.
No, Google Pay is a digital wallet. It’s a service that securely stores your customer’s payment details. When a customer uses Google Pay on your site, the transaction is still processed by a separate payment gateway. This makes the checkout faster for your customers.
Yes, PayPal is both a payment gateway and a payment processor. For many small businesses, it offers an all-in-one solution. It securely authorizes payments and then handles the transfer of funds.
The cost can vary a lot. It usually combines a one-time setup fee, a recurring monthly fee of around $10-$30, and a per-transaction fee. This fee is usually a small percentage of the total plus a flat rate.
The payment gateway is a secure tool that encrypts a customer’s payment data and sends it to the processor. Unlike a bank, the information it uses holds no monetary value whatsoever.
For international sales, you should look for gateways that support multiple currencies and many local payment methods popular in different countries.
Providers like Stripe and PayPal are well-known for their global reach and ability to handle a high volume of international payments but you’ll find many eCommerce site builders often take this into account too.
Payment gateways handle subscriptions through a process called tokenization.
When a customer makes their first payment, the gateway replaces their sensitive card information with a unique, non-sensitive string of characters called a token. This token is then securely stored and used for all future recurring payments.
Yes, a few modern payment gateways are starting to support cryptocurrency. They let businesses accept payments in Bitcoin or other digital currencies. When the customer pays with crypto, the gateway often handles the conversion to a fiat currency like USD before it’s deposited into your account.