Key takeaways:
- A dedicated IP address is an IP address exclusively assigned to one website or user.
- Dedicated IPs are ideal for sites sending high volumes of emails, requiring custom server configurations, or having consistent high traffic.
- A dedicated IP can enhance performance by reducing downtime risks, improving security, and ensuring smooth email communication.
You may have encountered the term “dedicated IP address” while setting up hosting or troubleshooting email issues. It sounds technical, but it’s relevant when building your online presence.
If you manage a website, handle emails, or run anything related to online performance, knowing how dedicated IPs work can help you make more informed choices in the future.
This guide breaks it down step by step, so you’ll know what a dedicated IP address is, when you might need one, and whether its pros outweigh the cons.
What is an IP address?
An IP address, short for Internet Protocol address, is a unique number assigned to any device connected to a network. It helps identify where data is coming from and where it needs to go.
Think of it like a street address for your website or computer. Just like a delivery service needs your home address to deliver a package, the internet uses IP addresses to deliver web pages, emails, and files to the right place.
IP addresses form the backbone of the internet’s infrastructure. Websites, devices, and servers use IP addresses to communicate with each other.
An IP address has two versions:
- IPv4, which looks something like 192.0.2.1
- IPv6, a newer format like 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334
IPv4 is the most widely used format and supports around 4.3 billion unique addresses. But since the digital landscape is expanding and we’re running out of IPs, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) developed IPv6 to handle the growing number of devices needing to connect online.
Most people never interact with IPs directly, and that’s thanks to the Domain Name System (DNS).
How does DNS relate to IP addresses?
Every website has an IP address. To visit a website, you have to type in the correct IP. However, memorizing and typing several numbers is not exactly user-friendly. That’s where DNS comes in.
The system pairs the IP with a domain name, like yourwebsitename.com, so each time you visit a webpage, you only need to type in the website name instead of the IP address.
Technically, DNS translates the domain name into the correct IP address. It tells the browser where to retrieve the information to display on your screen.
How IP addresses work
When a device connects to a network, your internet service provider (ISP) assigns it an IP address. This IP address can be private or public. In most home setups, your router receives a public IP from your ISP and then assigns private IPs to each connected device in your network.
IP addresses for websites have a slightly different process. Your hosting provider assigns your site an IP address, which the domain system uses to ensure browsers find it.
Types of IP addresses
| Category | Type | Description |
| Consumer IP address | Public IP | Assigned by your internet provider. Visible to the outside world. |
| Static IP | A fixed public IP that doesn’t change. Useful for remote access or hosting. | |
| Dynamic IP | Changes each time you reconnect. Most home users have this by default. | |
| Private IP | Used only within a local network. Lets devices like laptops and printers communicate. | |
| Website IP address | Shared IP | Used by multiple websites on the same server. Common in shared hosting. |
| Dedicated IP | Assigned to a single website. Offers better control, security, and email reputation. |
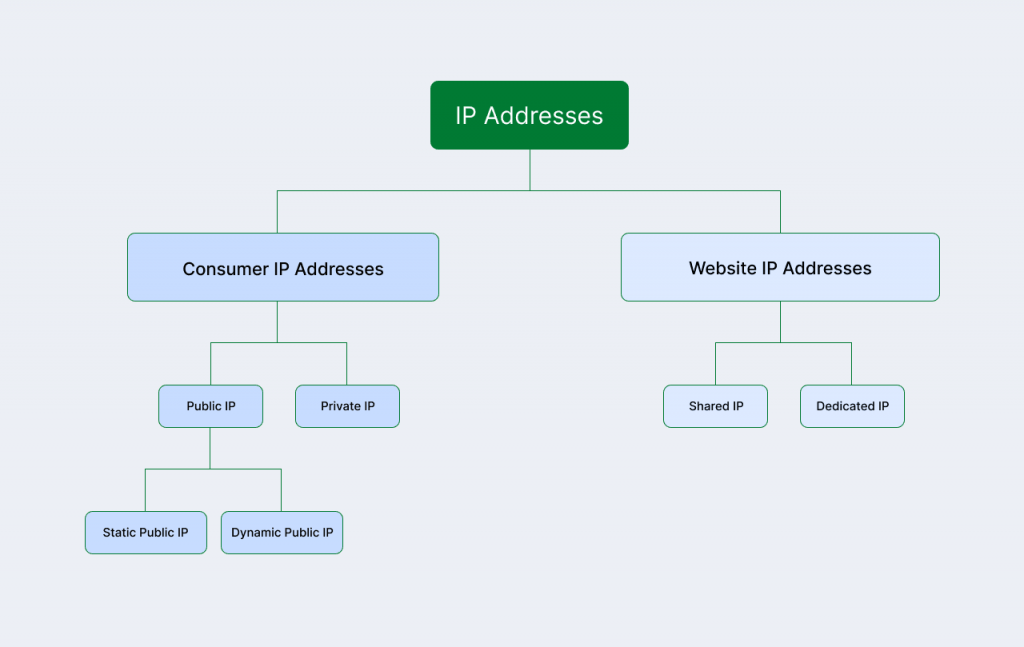
IP addresses have several different types, each serving different purposes. These types fall into two major classifications: Consumer IP address and Website IP address.
Consumer IP address
Consumer IP addresses are commonly used for personal networks, devices, and home internet connections. They help connect individual devices to the internet and manage local network traffic. These addresses can be private or public.
Public vs private IP address
Your internet service provider assigns a public IP address to your network. This is the address the rest of the internet sees when you browse websites or send emails. It can be further classified into static and dynamic IP addresses.
- Static IP address. This public IP address is a fixed, unchanging address that a user or network administrator assigns to a device or network. Once set, the entity gets the same IP address, regardless of how often you disconnect and reconnect to the internet.
- Dynamic IP address. A dynamic public IP address is temporary and can change each time you reconnect to the internet. ISPs typically assign dynamic IPs to users to conserve IP address space and reduce cost. When you connect to the internet, your ISP assigns a public IP to your connection. It resets if you restart your router or reconnect after being disconnected. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) automatically assigns an available IP address from a pool of addresses.
On the other hand, a private IP address is only used within a local network. They allow devices like your laptop, phone, or printer to communicate with each other without needing to use a public IP. Private IPs help create a secure and efficient network for your devices. Your router or local network assigns a private IP address to your connected devices.
Website IP address
A website’s IP address identifies your website on the internet. It’s what allows browsers to connect to your site. You can classify it into two types: dedicated and shared IP addresses:
Shared IP vs dedicated IP address
A shared IP address is an IP used by multiple websites hosted on the same server. In shared hosting environments, your website shares the server’s resources, such as CPU and memory, with other sites, and they all use the same IP.
When a user inputs a domain name into their browser, the server’s DNS routes the request to the appropriate website according to the domain name. Thanks to the domain name and DNS, the server knows which website the request is meant for, even though multiple sites are hosted on the same IP.
A dedicated IP address, on the other hand, is assigned exclusively to one website or server. This means your website will have its unique IP address, separate from any other site, even if hosted on the same server. You can acquire a dedicated IP with an additional fee through an ISP, virtual private network (VPN) service, or hosting provider.
Benefits of a dedicated IP address
A dedicated IP address offers numerous advantages for websites, especially those that handle sensitive data, require higher performance, or need more control over their hosting environment. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits:
- Better control. A dedicated IP gives you more control over your website’s security. You can adjust security settings, such as firewalls, access restrictions, and VPNs, according to your needs.
- Enhanced email deliverability. A dedicated IP helps ensure your emails maintain a good reputation. If another site on the same IP is flagged for sending spam, yours could also be flagged, resulting in your emails ending up in the spam folder.
- Better website reputation. Websites on a shared IP may suffer if another site on the same IP is flagged by search engines for spam or malicious behavior. A dedicated IP ensures that your website’s reputation is not tied to others.
- Exclusive remote access. A dedicated IP allows for exclusive, secure remote access to your website or server via file transfer protocol (FTP) or VPN. This function can be handy for website managers or developers who need to access the site securely without interference from other sites in a shared environment.
When do you need a dedicated IP address?
A dedicated IP address offers plenty of benefits, but not every website needs one. Investing in a dedicated IP address is the right choice if you find yourself in any of the following situations.
- Running an eCommerce website. A dedicated IP address can boost security and performance if you run an online store. eCommerce sites handle sensitive data and need to ensure a secure connection between your customers and your site. When your website has its own IP address, it’s less likely to be affected by other websites on the same server that may engage in malicious activities.
- Sending a high volume of emails. A dedicated IP ensures better email deliverability if your website handles a lot of email traffic. If one user is flagged for sending spam on a shared IP, all other users sharing that same IP are affected, damaging your domain name’s reputation.
- Custom server configurations. A dedicated IP address is necessary if you require custom server setups, like special configurations for FTP. Many businesses use FTP for secure file sharing or remote server access. A dedicated IP ensures that only your devices can connect to these services without interference from others in a shared environment.
- Running a large, high-traffic website. Websites with significant traffic typically require a dedicated IP to ensure smooth performance. A dedicated IP separates your website from the activities of other sites within the same server. This reduces your risk of getting negatively affected by others’ actions.
Disadvantages of a dedicated IP address
A dedicated IP address also has some downsides. It’s important to weigh these factors against your needs before deciding if it’s the right choice for you.
- Higher cost
- Limited availability in shared hosting plans
- Increased complexity for smaller websites
- No significant return on investment for low-traffic sites
Let’s delve into the details.
Higher cost
One of the main drawbacks of a dedicated IP is the cost. Since a dedicated IP is exclusive to you, it usually involves an extra monthly fee on top of your hosting plan. This is a significant factor for smaller businesses with tight budgets.
Limited availability in shared hosting plans
Dedicated IPs are usually offered with virtual private servers (VPS) or dedicated hosting plans, but are often unavailable with shared hosting plans. If you’re on shared hosting, you might need to upgrade to a higher-tier hosting plan to access a dedicated IP.
Increased complexity for smaller websites
Managing a website with a dedicated IP comes with added responsibilities. If you’re managing a simple website or a small, personal blog, the added complexity of an IP address configuration might overwhelm you. It may not be worth the time and energy for your current needs.
No significant return on investment for low-traffic sites
If your website doesn’t have significant traffic or security needs, you may not notice a big difference in performance with a dedicated IP. In many cases, a shared IP with a reputable hosting provider will be more than enough, and a dedicated IP may not deliver the expected return on investment.
Set your website up for success
A dedicated IP address offers several benefits, especially if you run an eCommerce website, handle a lot of email traffic, or manage a high-traffic site. Understanding when and why you need a dedicated IP helps you make more informed decisions for your business.
As you consider your hosting needs, it’s important to have a reliable partner that can support you every step of the way. Network Solutions offers website hosting, domain, and email services to ensure your online business runs smoothly. With our comprehensive services and dedicated support, you can leave the technical complexities to us while you focus on what matters most.
Frequently asked questions
A dedicated IP is perfect for businesses or individuals who require reliable, exclusive access for things such as sending high volumes of emails, secure remote logins, or protecting themselves from blacklisting issues caused by other users sharing the same IP.
Not directly, but it can enhance security, reduce downtime risk in high-traffic scenarios, and ensure smoother email deliverability for better user experience.
Depending on DNS propagation and hosting provider processing, it takes at least 24–48 hours to activate a dedicated IP address.
Yes, a dedicated IP can be traced to the hosting provider and sometimes to the website owner, especially if domain details are public. Using domain privacy and secure hosting can limit exposure.
You can request one through your hosting provider, domain registrar, or VPN service. It usually comes as an add-on to a hosting plan for an extra fee.