Key takeaways:
- An IP address is a group of numbers assigned to every internet-connected device.
- There are two versions of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6.
- IP addresses can also be vulnerable to threats online.
IP addresses are a unique string of numbers. Every online device needs one to receive and transmit data.
Understanding IP addresses isn’t as complicated as it sounds. In this article, we’ll explore what IP addresses are, why they matter, and how they affect your online activity.
What is an IP address and why does it matter?
An IP, or Internet Protocol, address, is a string of numbers that internet service providers (ISPs) assign to every online device. It allows communication and data transmission between different devices to run smoothly and efficiently.
Here’s what a typical IP address might look like:
192.0.2.126
Some IP addresses have periods that separate numbers, while others use colons. This depends on the version (IPv4 or IPv6).
IPv4 addresses use periods to separate numbers, while IPv6 addresses use colons, for example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
IP addresses play an important role in digital communication. They’re the reason why we’re able to load websites, send emails, and have a chat over the internet.
How does an IP address work?
Like humans, computers communicate by speaking the same language. However, they talk through numbers or IP addresses instead of words.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is a governing body that oversees the production and allocation of IP addresses. IANA distributes blocks of IP addresses to Regional Internet Registries (RIRs), who then assign them to your ISP.
When your device connects to your ISP, it’s automatically assigned an IP address. As you access a website or online service, servers will use that IP address to locate your device and deliver your requested content.
However, your IP address isn’t always static. It can change depending on your connection method, location and network. Some may have static IPs that remain constant.
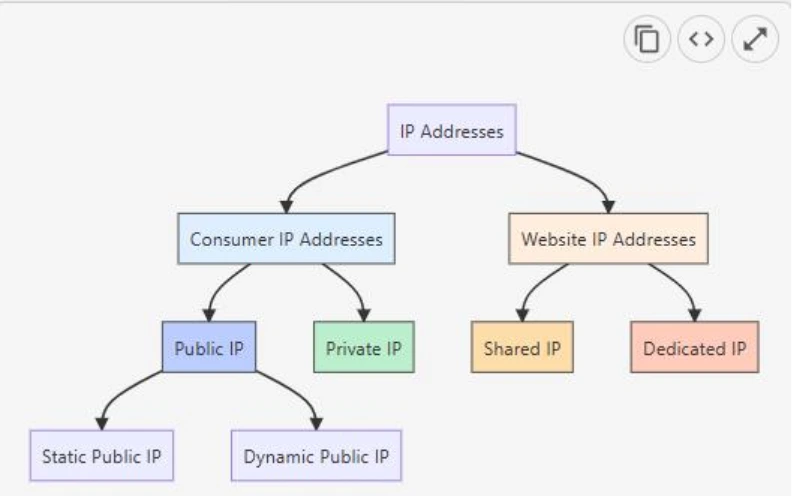
What is a Private IP address?
A Private IP address is your device’s own unique identifier, also known as a local IP address.
These Private IP addresses don’t connect directly to the internet and are not visible online. Instead, your home network uses this IP to identify devices within your local network. This way, your home network can direct traffic to the correct device.
What is a Public IP address?
A Public IP address is exactly what its name suggests. It’s your device’s publicly visible address. ISPs assign public IP addresses to your router, giving your home network access to the web.
Public IP addresses come in two types: dynamic and static IP addresses.
Dynamic IP address vs Static IP address
| Feature | Dynamic IP address | Static IP address |
| Definition | An IP address that changes periodically. | An IP address that remains constant. |
| Assignment | Assigned automatically by ISP from a pool. | Assigned manually or reserved permanently. |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective for ISPs. | Usually more expensive, may have additional fees. |
| Use Cases | Regular home users, casual internet browsing. | Businesses hosting servers, remote access, VOIP, or VPNs. |
| Security | Changing IPs can add privacy by making tracking harder. | Easier to set up secure, consistent connections. |
| Management | Easier for ISPs to manage limited IP resources. | Requires manual configuration and management. |
| Reliability | May occasionally change, causing possible interruptions. | Consistent and reliable connectivity. |
| Visibility | Publicly visible when connected to ISP, changes over time. | Publicly visible and constant over time. |
Dynamic IP addresses change constantly, while Static IP addresses remain the same. To understand how they work, let’s dive deeper.
Dynamic IP addresses are public IP addresses that change periodically. ISPs typically buy a large pool of IP numbers, which they re-assign regularly. They continuously recycle addresses to keep expanding their access to potential customers.
Dynamic IP addresses are cost-effective, allowing ISPs to manage a limited number of IP addresses by reusing them as devices go offline.
It’s also beneficial to use a dynamic IP address. Changing IP addresses makes it harder for potential attackers to track a device.
Static IP addresses, on the other hand, stay the same until they’re manually changed.
This type of public IP address is ideal for businesses that require a permanent address. Static IP addresses offer better reliability for businesses that need consistent access to their devices or networks.
Here’s a recap of the “types of IP addresses” that we just covered:
IPv4 vs IPv6: What’s the difference
IPv4 and IPv6 are two different versions of IP. Let’s break them down.
| Feature | IPv4 | IPv6 |
| Full Name | Internet Protocol version 4 | Internet Protocol version 6 |
| Address Length | 32 bits | 128 bits |
| Address Format | Four decimal numbers separated by periods | Eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons |
| Example Address | 192.0.2.126 | 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 |
| Number of Addresses | Approximately 4.3 billion | Approximately 3.4 × 10^38 (vastly larger) |
| Address Exhaustion | Nearly exhausted due to device growth | Designed to solve exhaustion problem |
| Deployment | Widely used, legacy protocol | Increasing adoption, especially for new networks |
| Security | Security optional, often added via extensions | Built-in IPsec support for better security |
| Configuration | Manual or DHCP | Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) and DHCPv6 |
| Routing | Broadcast, subnetting supported | No broadcast; uses multicast and anycast instead |
IPv4, or Internet Protocol version 4, is the first version of the Internet Protocol. Here’s an example of what an IPv4 looks like:
192.0.2.126
It’s a set of four numbers separated by decimals.
IPv4 is also known as the 32-bit system since it can handle 32-bits of information. This allows for approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. While sufficient at the time, its pool is nearly exhausted due to the rapid growth of internet-connected devices today.
This is where IPv6 comes in. IPv6 is the newer version of the Internet Protocol. Launched in 1998, IPv6 addresses the exhaustion of IPv4 identifiers.
IPv6 has 128 bits of total storage and can support a larger number of unique IP addresses, over a thousand times more than IPv4’s 4.3 billion. This expanded capacity is capable of supporting the growing number of internet-connected devices.
IPv6 numbers look similar to IPv4 with one exception, they use colons as separators instead of periods.
Here’s an example of what IPv6 looks like:
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:733
IP addresses for websites
Like each device, websites also have their own IP addresses. This way, when users enter a domain name, they’ll be redirected to the correct website server.
Websites use two types of IP addresses:
- Shared IP addresses: Multiple websites hosted on the same server share a single IP address. This is common in shared hosting environments where many sites coexist on one physical server.
- Dedicated IP addresses: A website (or server) has its own unique IP address assigned exclusively to it. This allows the website to be accessed directly via its IP address alone (without relying on a domain name).
Websites on a shared server will have a shared IP address, while a website with a dedicated server gets its own IP address.
How to find your IP address
Finding your IP address varies depending on the type of IP address you’re looking for.
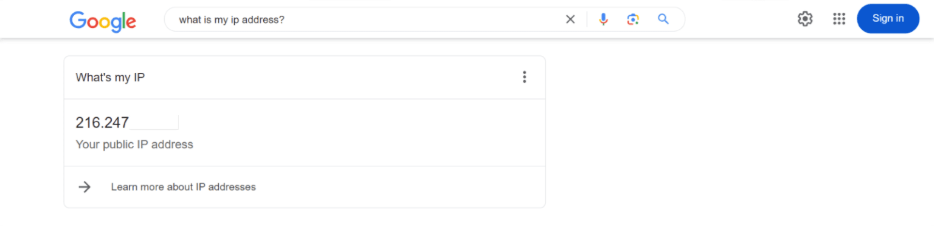
You can look for your public IP address easily by searching “What is my IP address?” on Google.
You’ll see your IP address at the top of the page. In other cases, you might have to scroll down a bit to see it.
If you’re looking for your private IP address, the process is going to be slightly different based on your operating system (OS).
Finding your Private IP address on Windows devices
To find your private IP address on Windows, follow these steps:
- Go to the Windows search bar; type cmd. This will open a pop-up box, known as Command Prompt.
- Type ipconfig to find your IP address.
Finding your Private IP on Mac devices
For Mac users, select network in the System Preferences. You should immediately see your IP address.
Finding your phone’s Private IP address
Just like using a desktop device, finding your private IP address on your mobile device will depend on your phone’s OS.
For Android users
- Go to your Wi-Fi settings
- Click on the network’s name
- Click view more. Here, you’ll find your IP address along with other information related to your network connection.
For iPhone users
- Go to settings.
- Click Wi-Fi
- Click your network’s name to open its information. Your IP address should appear once you’re in your network details.
Common IP address security threats
Since IP addresses play a very important role in internet communication, it’s usually the target for online threats like:
- DDoS attack
- IP spoofing
- Online stalking
DDoS attack
The most common cyber threat is the distributed denial of service (DDoS). Cybercriminals conduct a DDoS attack to overwhelm a website, device, or network. They do this by flooding a website with high traffic from highly infested machines.
This type of attack usually targets businesses. However, individuals like online gamers and streamers are prone to a DDoS attack since their IP addresses are visible through their screens.
IP spoofing
IP spoofing involves the forging of IP addresses. Hackers will hack your IP address and use it for malicious purposes, such as downloading pirated music, movies, and videos with sensitive content.
IP spoofing can breach your ISP’s terms of use, which could attract the attention of law enforcement.
Online stalking
Any activities online can reveal your IP address. If your IP address is not protected, hackers can use it to track your location.
It’s important to note that a person cannot track your exact address but can only locate your general area. However, with the help of hacking and social media platforms, they could successfully find your home.
4 ways to protect your IP address
There are a few effective ways to protect your IP from online threats. This includes:
- Using a proxy server
- Using a VPN
- Avoiding malicious content
- Using an anti-virus solution
Using a proxy server
A proxy server acts as a middleman between your device and the internet. A proxy server routes your online activity to a different server. This way, when you visit a website, the site will only see the proxy server rather than your actual IP address.
However, some proxies will spy on you. So, it’s important to choose a reliable and reputable one.
Using a VPN
A VPN, or virtual private network, hides your IP address by routing traffic through secure servers from different regions. VPNs also prevent your Internet Service Provider and hackers from monitoring your activities online.
Using a VPN is beneficial in the following situations.
- When using a public WI-FI
- When traveling to a foreign country
- When working remotely
- When you want some privacy
Avoiding malicious content
Completely avoiding untrusted websites can protect your IP address. Simply clicking on unknown links can expose your IP address, so it’s best to avoid them.
Avoid downloading suspicious files as well. Hackers often embed malware in downloadable content to track your IP, steal data, and launch attacks.
Using an antivirus solution
A reliable antivirus solution can help you detect and remove malware and block malicious programs that aim to exploit your IP address.
For website owners, integrating SiteLock into your website will help you encrypt your data and prevent it from exposure. This goes beyond protecting your website; it also protects your customers’ data.
Stay secure online
Learning more about IP addresses and how to protect them is one step closer to a safer online journey. Understanding digital security empowers you to take charge of your privacy and security.
Explore Network Solutions to find out more about your online security. With comprehensive guides and extensive knowledge-based articles, we help you stay informed and secure while surfing the internet.
Frequently asked questions
Every device connected to your WI-FI router will have its own private IP address. Your router will also have its public IP address to navigate the internet.
Yes. You can block an IP address, especially if that address is unusual and is causing suspicious traffic.
Devices in different internal networks can have the same private IP address. However, there are no devices that share the same public IP addresses.
Your private IP address can start with 10.x.x.x, 192.168.x.x, and 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255. You can check your private IP address through your device’s settings.
No. Although your IP address links to a geographical location, it’s not specific enough to find you.