Key takeaways:
- DKIM stamps your domain on every message. That proof shows you’re legit and shuts down spoofing attempts.
- It works with SPF and DMARC to block phishing emails and help your messages land in inboxes.
- DKIM gives you control over email authentication and protects your brand from impersonation.
One fake email is all it takes to hijack your data. Over 90% of cyberattacks trace back to a single phishing email. It sneaks in, looks legit, and sets the trap. DKIM helps stop this. It adds a digital signature that confirms the message came from your domain, not from a scammer. This keeps your brand safe, and your emails trusted.
Let’s better understand what DKIM is, how a DKIM record works, and what it does to email deliverability and security.
What is DKIM?
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) is an email authentication method that helps the recipient’s mail server confirm two things:
- Who sent the email (an authorized domain), and
- That the message wasn’t changed in transit.
It works by attaching a digital signature to each outgoing message. The recipient’s server looks up the sender’s public key in DNS and uses it to check that the signature matches. If it does, the message is verified as genuine and untampered.
How does DKIM work?
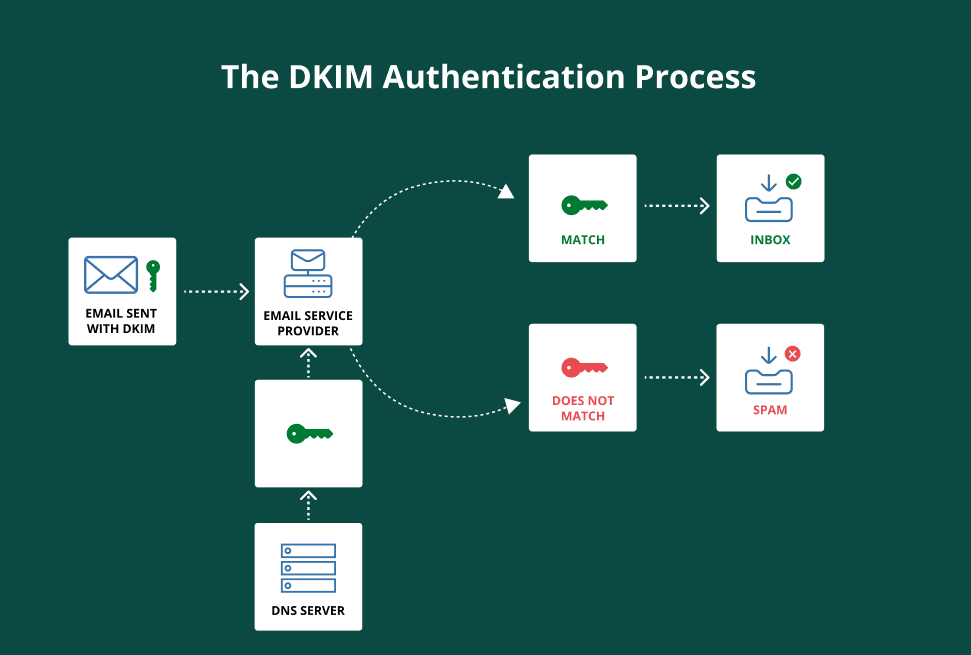
DKIM adds a hidden signature to every message. When it’s received, the email server checks that signature against your public key stored in DNS.
Here’s how that process looks:
- Your mail server signs the email header using a private key.
- The recipient’s server looks up the DKIM record in DNS to find your public key.
- If the signature matches the public key, the message is marked as valid.
This email authentication step links each message to your domain and helps make sure it stays safe on the way to the inbox.
What is a DKIM record?
A DKIM record is a DNS entry that validates your email’s signature. It helps mail servers confirm the message is original and came from your domain.
Each DKIM record includes:
- Name. Combines the selector and your domain (e.g., selector._domainkey.example.com).
- Record type. Always set to TXT.
- Content. A string containing the public key.
Here’s an example of a DKIM TXT record:
default._domainkey.example.com IN TXT
“v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQ…”
A strong DKIM record gives your email setup real protection. It keeps spoofers out and helps your messages pass authentication every time.
What is a DKIM selector?
A DKIM selector helps receiving mail servers find the correct public key stored in your DNS to verify a DKIM signature. This tag lives in your DKIM record and points to the key pair your server uses to sign outgoing emails.
For example, the selector forms part of the record name:
default._domainkey.example.com
This is just the label or name that tells email servers where to look for your DKIM information.
The full record it points to includes details like the version, the type of key, and the actual public key used to check your email is real and unchanged.
DKIM vs SPF vs DMARC
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) are two other email authentication protocols that work with DKIM to stop phishing and spoofed emails.
- SPF checks if a message is sent from an authorized email server by verifying its IP address against the domain’s list.
- DMARC works with SPF and DKIM to tell mail servers what to do with messages that fail these checks (reject, quarantine, or allow).
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Protocol | Purpose | Setup | Benefits |
| DKIM | Uses a digital signature and key pair to verify the email’s content and domain. | Adds a DKIM record with your public key in DNS. | Confirms the message hasn’t been altered and improves email authenticity. |
| SPF | Validates that the sending mail servers are authorized to use your domain. | Publishes a TXT DNS record listing permitted servers. | Stops unauthorized servers from sending fraudulent emails. |
| DMARC | Defines policies for failed SPF or DKIM checks. | Creates a DMARC record with actions like reject or quarantine. | Blocks malicious emails and provides reporting on suspicious activity. |
Why DKIM matters for email security
Using DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) helps protect your reputation and gets your emails where they’re meant to go.
Here’s what it does:
- Stops spoofing and phishing. DKIM attaches a cryptographic digital signature to every message. This makes it tougher for attackers to fake your domain or send malicious emails pretending to be you.
- Improves email deliverability. When an email server sees a valid DKIM record, it recognizes the message as legitimate. This reduces the chance of your emails being flagged as spam and improves email authenticity.
- Builds trust and brand credibility. Verified messages show recipients that your communications are genuine and not email fraud. This trust is vital for marketing campaigns, transactional emails, and newsletters.
- Enhances reporting and control. DKIM works together with DMARC records and sender policy framework (SPF) to provide better insight into who is sending mail on your behalf. Together, these protocols help you track and block unauthorized activity.
Without DKIM, you leave the door open for attackers to misuse your domain. Adding it is one of the simplest ways to protect your brand and help your emails reach the inbox.
How to set up DKIM for your domain
Setting up DKIM backs your identity and protects your domain from impersonators. Here’s what to do next:
- Generate your DKIM records. Use your email provider to create a key pair (private and public key) or retrieve the DKIM values they provide.
- Log in to your DNS settings. Open your DNS manager from your hosting provider or registrar where your domain is pointed.
- Add a new TXT or CNAME record. Use the Network Solutions DNS Manager or your provider’s DNS console to create the record. Make sure to match the DKIM selector (usually part of the host name) to what your email provider specifies.
- Paste the DKIM value. Enter the full DKIM string, including tags like v=, k=, and the public key (p=), into the value field.
- Save your changes. Submit the record and allow time for DNS propagation—this may take a few minutes to 48 hours.
- Test the setup. Use a DKIM checker tool or send a test email to confirm that the DKIM record is working properly.
- Enable DKIM signing. Go back to your email platform and switch on DKIM signing to start adding signatures to all outgoing messages.
This setup helps protect your email messages and keeps them verifiable.
Common DKIM issues and how to fix them
DKIM isn’t foolproof. Here’s what to watch out for and how to strengthen your setup.
- DKIM isn’t enough. DKIM authentication is just one layer. To block spoofing and phishing attacks, you’ll also need SPF and DMARC.
- Test your record. Use tools like MXToolbox, Skysnag, or a DNS propagation checker to confirm your DKIM record is active, and the public key is published. This helps verify that your email authentication is working.
- Failed DKIM hurts. It can trigger spam filters, block delivery, and hurt your sender reputation.
DKIM is your first line of defense. SPF and DMARC complete your security measures. Add all three to keep your domain safe and your emails trusted.
Secure your emails with a strong DKIM signature
DKIM signs every email you send. It proves your messages are real and blocks fake ones. It improves deliverability, shields your domain, and keeps phishers out.
When combined with SPF and DMARC, it gives your emails even stronger protection.
Ensure every email you send is signed with DKIM, which proves your messages are real and blocks fake ones. This, combined with our secure email hosting infrastructure, improves deliverability, shields your domain, and keeps phishers out.
And if you need help in setting up your inbox, check out our step-by-step guide on how to set up an email from a domain.
Frequently asked questions
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is a way to tag your emails with proof that they’re really from you. It adds a code to each message, and when it arrives, the receiving server checks if that code matches what’s in your domain records. If it lines up, the message is treated as safe and unchanged.
SPF checks where an email comes from and confirms the server is allowed to send mail for your domain. DKIM confirms the message content is safe and came from your domain without changes. Both help prove your email is real and trustworthy.
You need a DKIM record to prove that your emails are real and came from your domain. It helps block spoofing, boosts deliverability, and protects your brand by making sure your messages aren’t altered or faked during transit.
To set up DKIM, you first create a key pair through your email provider. Then, add the public key to your domain’s DNS as a TXT record. Once that’s done, turn on DKIM in your email settings to start signing outgoing messages.
DKIM isn’t a strict requirement, but skipping it puts your emails at risk. Without it, your messages could get flagged or land in spam, which hurts your trust score and inbox reach.
When an email fails DKIM, the receiving server sees it as suspicious. It can land in the spam folder, get blocked, or lose trust with inbox filters. This affects your email reach and can hurt your sender reputation, especially if you rely on email for business or marketing.
You can send emails without DKIM, but they’re more likely to be flagged or distrusted. That affects how often your emails land and how credible your domain looks.
About 1.2% of all emails sent are phishing attacks, according to a 2024 report. It may sound small, but millions of dangerous emails are sent every day. That’s why DKIM and other protections matter.




