Key takeaways:
- HTTP Error 403, also known as the 403 forbidden error, often happens when a server denies access to a web page.
- Common causes include file permission issues, misconfigured settings, or security restrictions.
- Fixing a 403 error involves checking file permissions, security settings, plugins, and CDN configurations to restore access.
You click on a link, expecting to land on a web page. But instead, a 403 forbidden error pops up on the screen. Frustrating, right?
The 403 Forbidden error, also known as HTTP Error 403, means that access to the page is blocked. As a user, it can be annoying, especially when you’re trying to access important information. And if you happen to be a website owner, resolving this issue is just as necessary. Even a minor error like this can deter site visitors and negatively impact your SEO rankings.
In this guide, we’ll explain the HTTP Error 403, explore its causes, and provide all possible solutions. So, the next time you run into this issue, you’ll know exactly what to do.
What is the 403 forbidden error?
An HTTP Error 403, or 403 Forbidden error, is a status code that means the server is blocking access to the page you’re trying to reach. The server understands your request, but it refuses to load the content because you don’t have permission to view it.
In most cases, HTTP Error 403 means:
- The website’s security settings or permissions are blocking access
- You don’t have valid authentication credentials
- Your IP address or region might be restricted from viewing the page
Note: HTTP Error 403 differs from other common HTTP status codes. For instance, a 404 status code means the page doesn’t exist at all, while a 403 indicates that the page does exist, but access is explicitly blocked.
On the other hand, if the issue is on the server’s side, rather than a permissions problem like a 403, it’s a 500 Internal Server Error.
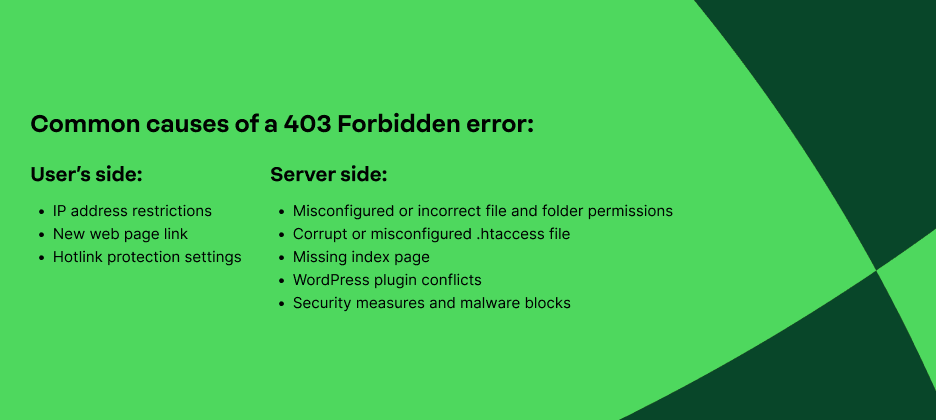
What are the common causes of a 403 Forbidden error?
In many cases, a 403 Forbidden error happens due to issues on the user’s end. When your browser sends a request that the server can’t authorize, the system blocks access and returns this status code.
Common reasons why website users might encounter this HTTP status code include:
- IP address restrictions
- New web page link
- Hotlink protection settings
While many 403 Forbidden errors start on the user’s side, server configurations can also trigger the same response. When the server’s settings prevent a request from being processed, it may block access even if the page exists.
Common server-side causes of the HTTP Error 403 include:
- Misconfigured or incorrect file and folder permissions
- Corrupt or misconfigured .htaccess file
- Missing index page
- WordPress plugin conflicts
- Security measures and malware blocks
IP address restrictions
Sometimes, your IP address or location is why you can’t access a website. Some websites limit access based on geography or specific IP addresses, so you’ll likely encounter a 403 status code if yours is on the blocked list.
This error code also appears when the domain name is incorrectly pointed to the wrong IP address. If the website has recently moved to a new server and hasn’t updated its DNS records yet, your browser may be trying to access an outdated site version, which is no longer accessible.
New web page link
If a webpage’s link has recently changed, but your browser or a search engine still has the old version cached, you might run into a 403 error code. This happens because the page you’re trying to access no longer matches the stored link.
Hotlink protection settings
When you try to display an image from another website but end up with a broken link or an error message, it’s primarily because of hotlink protection. Some websites prevent other sites from embedding images or files using this feature.
If a site has enabled hotlink protection and another site tries to display its images or files without permission, the request gets blocked.
Misconfigured or incorrect file and folder permissions
Every file and folder on a website has unique file permissions that basically determine who can view, edit, or execute them. If these necessary permissions aren’t set correctly, your site’s server may block access, which triggers a 403 status code error.
For example, a website owner might restrict access to certain files for security reasons or accidentally misconfigure the settings. This, in turn, prevents even authorized visitors from accessing the content. In some cases, web hosting services set strict default permissions that need to be adjusted manually.
Corrupt or misconfigured .htaccess file
The .htaccess file, in essence, is a server configuration file that helps control how a website functions, including access permissions. If this file contains incorrect settings or has been altered, the server may not be able to handle requests properly and will block access to certain pages or even the entire site.
Missing index page
Most websites rely on a default homepage file, typically named index.html or index.php, to load when a visitor accesses the site. And if this file is missing or named incorrectly, the server won’t know which page to display. As such, instead of showing the homepage, it may block access entirely.
WordPress plugin conflicts
If your WordPress website shows a 403 status code, a faulty plugin could be the reason. Some security plugins have strict settings that can mistakenly block access to certain pages and, worse, even lock you out of your own website.
Another possible issue is with the wp-content folder, where your themes and media files are stored. If WordPress can’t access this folder due to incorrect permissions or plugin conflicts, it can trigger a 403 Forbidden error.
Security measures and malware blocks
In some instances, you see the same error code because of malware infections corrupting key site files. Malware infections may cause repeated access issues until the infection is removed.
How to fix an HTTP Forbidden Error 403 (for website visitors)
If you’re seeing an HTTP Error 403 while browsing, there are several steps you can try before diagnosing the website as the problem.
Here are solutions that often resolve the issue for visitors:
- Refresh the web page
- Double-check the URL
- Clear your browser cache and cookies
- Disable browser extensions
- Try using a different browser or device
- Check if your IP address is blocked
Solution 1: Refresh the web page
Let’s start with the simplest fix: simply refreshing the page. Sometimes, a 403 Forbidden error is just a temporary glitch caused by a connection issue or a misloaded page.
Here’s what to do:
- Press F5 (Windows) or Command + R (Mac) to reload the page.
- If that doesn’t work, try closing and reopening your browser, then revisit the site.
Solution 2: Double-check the URL
Before trying anything else, make sure you’ve entered the correct web address. More often than not, that’s all it takes to fix the problem!
A tiny typo, like an extra slash or a missing file extension, will point you to a restricted directory instead of an actual page. So, here’s what to do:
- Look for any extra slashes (//), typos, or missing extensions (.html, .php).
- Try simplifying the URL and removing parts of it to see if the main site loads (e.g., example.com/protected-page → example.com).
- If you clicked a link and received an error, go to the homepage instead and try navigating from there.
Solution 3: Clear your browser cache and cookies
Your browser might be holding onto outdated site data, which can sometimes cause access issues and trigger a 403 error code. When you clear your cache and cookies, it forces the browser to load the most up-to-date version of the site, which might resolve the problem.
Here’s how to clear cache and cookies:
For Google Chrome:
- Open Chrome and then click on the three-dot menu in the top-right corner.
- Go to Settings, then choose Privacy and Security.
- Click Delete browsing data.
- Select cookies, other site data, and cached images and files.
- Click on “Clear data,” restart your browser, and try accessing the site again.
The steps are similar for Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Under privacy settings, look for the option to clear browsing data.
Solution 4: Disable browser extensions
Some browser extensions, especially ad blockers, privacy tools, or security add-ons, can block access to specific websites. To identify if one is the culprit, disable it for a while.
To disable extensions in Google Chrome, follow these steps:
- Click on the three-dot menu in the top-right corner.
- Go to Extensions, then select Manage Extensions.
- Toggle off extensions one by one and reload the page after each.
- If the website starts working, the last disabled extension is likely the cause of the issue. You can either remove it or adjust its settings to allow access.
For Firefox, Edge, and Safari, you’ll find extension settings under their respective menus.
Solution 5: Try using a different browser or device
Are you still seeing the 403 Forbidden error? Open the website using a different browser. Switch from Chrome to Firefox, Edge to Safari, or even use incognito mode. You can also check on another device, such as your phone or tablet.
If the site works on another browser, the issue is likely due to cache, cookies, or extensions on your primary browser. And if it loads fine on another device but not on your Wi-Fi, your IP address might be blocked.
Solution 6: Check if your IP address is blocked
Some websites, unfortunately, block certain IP addresses due to security policies, geo-restrictions, or suspicious activity. If you think your IP is on the blocked list, here’s what you can do:
- Restart your router. If your internet provider assigns dynamic IP addresses, rebooting your router may result in a new one being assigned.
- Use a VPN or proxy to access the site from a different location and see if the error disappears.
- Find your IP address. Visit whatismyipaddress.com and note your public IP.
- If none of the above options work, contact the website administrator for assistance.

How to fix an HTTP Forbidden Error 403 (for website owners)
If you’re seeing an HTTP Error 403 on the website you’re managing, the issue is often tied to your server settings or site configuration.
Here are the most common fixes you can try to restore access:
- Check file and folder permissions
- Fix a corrupt .htaccess file
- Add or upload an index page
- Check if hotlink protection is misconfigured
- Scan for malware and security issues
- Check for plugin or theme conflicts (for WordPress users)
- Deactivate CDN temporarily
Solution 7: Check file and folder permissions
As each file and folder on your web server has proper permissions that control who can read, write, or execute them, setting incorrect permissions will prevent users from accessing your website.
To resolve this, you’ll need to make sure your files and folders have the right permission settings:
- Folders should be set to 755: This allows the owner to read, write, and execute, while others can only read and execute (but not modify the contents of the folder).
- Files should be set to 644: This allows the owner to read and write, while everyone else can only read the file.
Here’s how to fix file permissions:
Option 1: Using cPanel
- Log in to your hosting account’s cPanel.
- Go to Websites, then select Manage.
- Search for Fix File Ownership in the sidebar.
- Click on Fix File Ownership, mark the checkbox, and click Execute. This will reset all files to 644 and folders to 755, restoring the default permissions.
Option 2: Using File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Connect to your site via FTP/SFTP using a client like FileZilla.
- Navigate to the root directory of your website, typically named public_html.
- Right-click on the folder containing your site and select File Attributes or Permissions (depending on your FTP client).
- Set folder permissions to 755. Then, select Recurse into subdirectories and apply the change to directories only.
- Repeat the process for files. Set the permissions to 644 and apply the change to files only.
- For added security, manually adjust the permissions for your wp-config.php file (for WordPress.org sites) to 440 or 400.
- Save changes and reload your website to check if the issue is resolved.
Important: Be cautious when changing permissions. Incorrect settings can either block access or expose sensitive files and data! If you’re unsure about file permissions, always check your hosting provider’s documentation or contact their support team before making any changes.
Solution 8: Fix a corrupt .htaccess file
The .htaccess file tells the server how to handle directives like redirects and security settings. If corrupt or misconfigured, it might block access to certain pages and trigger a 403 Forbidden error.
Luckily, fixing it is easy! You just need to delete the file and let your site create a new one.
Here’s how:
- Sign in to your website via FTP or cPanel File Manager.
- Search for the .htaccess file in your site’s root directory.
- Download your existing .htaccess file to create a backup.
- Delete the existing .htaccess file, or, for safer troubleshooting, rename it to .htaccess_backup.
- Repeat the process for files. Set the permissions to 644 and apply the change to files only.
- Try reloading your site. If it works, the file was the issue.
- Generate a new .htaccess file. Copy and paste the following code into the new file:
# Enable URL Rewriting
RewriteEngine On
# Rewrite rule to redirect requests to index.php
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ index.php?/$1 [L]If you’re using WordPress, here’s how to create a new .htaccess file:
- Go to the WordPress Dashboard.
- Choose Settings, then Permalinks.
- Click Save Changes. This automatically creates a new .htaccess file with the correct settings.
Solution 9: Add or upload an index page
All websites require a default index page (like index.html or index.php). Otherwise, the server won’t know which page to display and will just show a 403 Forbidden error.
Here’s what you should do:
- Check if you already have an index file. Open your website’s root folder (public_html) and look for index.html or index.php.
- Rename your site’s homepage. If your main page has a different name (like homepage.html), rename it to index.html or index.php using your hosting file manager or an FTP client.
- If an index file is missing, you need to create a new one.
- Go to your public_html folder.
- Then, create a new file and name it index.html or index.php.
- You can leave it empty for now or add basic content.
- Redirect to your actual homepage. If your main page isn’t named index.html, set up a redirect:
- Navigate to your root directory and open the .htaccess file.
- Add this line, but replace homepage.html with your actual page name:
Redirect /index.html /homepage.html
- Save the changes and refresh your site.
Solution 10: Check if hotlink protection is misconfigured
Let’s say you upload product images to your website. Another website copies the direct URL of your photos and displays them on its own site. Whenever someone visits their page, your images load from your server, using up your bandwidth instead of theirs.
Hotlink protection stops this from happening.
When hotlink protection is enabled, it typically returns a 403 Forbidden error. There’s no need to worry, as it’s just how this feature is supposed to work. But if it’s misconfigured, it might block your site from accessing its own resources.
Here’s how to disable or configure hotlink protection:
- Log in to cPanel.
- Click Hotlink Protection under Security.
- Check and adjust the settings. You have two options:
- Add your website’s URL to the list of allowed sites.
- Temporarily disable hotlink protection.
- Once you’ve updated the settings, refresh your website and check if the 403 error has been resolved. If the issue persists, another security setting might be blocking access.
Solution 11: Scan for malware and security issues
A 403 Forbidden error can sometimes be a sign of something more serious, such as malware or security threats. Malicious software can modify your .htaccess file, change permissions, or block access to certain parts of your website. If you suspect malware, running a security scan is often the best course of action.
Option 1: Use a security plugin (for WordPress sites)
- Install and activate a security plugin.
- Run a full malware scan to check for suspicious files.
- Follow the plugin’s recommendations to remove threats.
Option 2: Scan through your hosting provider
- Log in to your hosting control panel.
- Look for a section labeled ‘Security’ or ‘Malware Scan’.
- Run a full scan and check the results.
Solution 12: Check for plugin or theme conflicts (for WordPress users)
If you’ve already checked the usual suspects, such as your site’s settings, security rules, and server configurations, but you’re still running into a 403 error, check your WordPress plugins. Sometimes, an update, an outdated file, or a conflict between plugins can cause issues and block access to your site.
Here’s how to check for plugin issues:
If you can access your WordPress dashboard:
- Go to Plugins, then select Installed Plugins.
- Deactivate them all.
- Refresh your WordPress site to see if the status code error disappears.
If you’re locked out of WordPress:
- Connect to your website via FTP/SFTP (using FileZilla or your hosting file manager).
- Navigate to wp-content and find the plugins folder.
- Set the folder name to plugins-deactivated. This will disable all plugins.
- Check if your site loads correctly. If disabling all plugins resolves the error, one of them is likely causing the 403 Forbidden error.
- To pinpoint the problematic plugin, rename the plugins folder back to plugins.
- Reactivate plugins one by one and check your site after each activation.
- Once you identify the faulty plugin, update or remove it.
Solution 13: Deactivate CDN temporarily
If your site relies on a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up loading times, it might also be why you’re seeing a 403 Forbidden error. Sometimes, a CDN can cache errors due to issues like file permissions, IP blocking, or incorrect .htaccess rules.
To check if your CDN is causing the issue, try disabling it temporarily:
- Log in to your CDN provider’s dashboard.
- Look for CDN settings (this may be under “Performance,” “Caching,” or “Security”).
- Find the option to disable or pause the CDN, then turn it off.
- Clear your website’s cache and check if the 403 error is resolved.
- If the error disappears, the issue likely lies with your CDN configuration. You may need to adjust security settings, update cache rules, or contact your CDN provider for further assistance.
And if these steps feel too technical, consider using a managed hosting plan with 24/7 expert support so you always have help on standby when access errors appear.

Other variations of a 403 Forbidden error
Depending on the website and browser, you might see variations of 403 errors.
Error code | Description |
|---|---|
403 Forbidden | The web server understands your request but refuses to grant access to the page. |
403 Invalid Credentials | Access is denied because the credentials you’re using are unauthorized or incorrect. |
403 IP Blocked | The server restricts access to specific IP addresses and blocks those that are unauthorized or unrecognized. |
403 SSL Required | The web server requires a secure connection (SSL certificate) to access the page and blocks unsecured requests. |
Error 403 disallowed_useragent | The server blocks your request because you use an outdated or unsupported browser. |
In general, if you come across terms like ‘forbidden’ or ‘access denied’, you’re most likely dealing with an HTTP 403 error.
How to prevent HTTP 403 Forbidden errors and keep your website accessible
Fixing a 403 Forbidden error is one thing, but ensuring it doesn’t happen again will save you time and frustration in the long run.
Here are some best practices to keep your website working smoothly at all times:
- Regularly review file permissions to avoid accidental access restrictions.
- Keep plugins, themes, and software updated.
- Monitor your .htaccess file after updates or edits.
- Whitelist your IP when using security plugins.
- Use a reliable security plugin or malware scanner.
- Set up hotlink protection settings correctly.
- Configure your CDN properly.
- Perform regular site audits to identify and fix issues.
- Use security tools to prevent misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
You can also use tools to detect hidden access issues before they become a problem for others. You can use our SEO tool to scan your site for 403 errors, missing pages, and crawl issues that might affect your visibility.
Frequently asked questions
Not necessarily. A 403 Forbidden error simply suggests that the server understands your request but is denying access. It could be due to incorrect permissions, security settings, or other factors.
The server is blocking access to the web page or resource you’re trying to reach. As mentioned, it’s often related to permissions or security settings.
No, a 403 error doesn’t mean the site is down. It just means you’re not allowed to access the page. The website is still up, but access is restricted for some reason.
Not always. A 403 error could be due to other factors, like misconfigured file permissions or settings. If your IP is blocked, try restarting your router or using a VPN to test.
A 403 in HTTP means the server understands your request but is refusing to give you access. It’s a permission-related error, usually triggered when you’re trying to view a page or file you’re not authorized to access.
You may get a 403 Forbidden error on Chrome if the page link is outdated, your browser cache is holding incorrect data, or an extension is blocking the request. It can also happen if the website has restricted your IP address or the page is protected and requires permission to access.
Fix HTTP 403 Forbidden errors for smooth browsing
Running into an HTTP 403 error can be an unpleasant experience for site users and owners. But put your worries aside! Troubleshooting the right way can get your site back up and running in no time.
To keep your website performing well and protected, use reliable hosting, security tools, and expert support. With the right setup, you can avoid status code errors, such as the 403 Forbidden, and keep everything running smoothly without a hitch.
To gain a deeper understanding of various status codes and their implications for your site, refer to our guides on the different HTTP status codes and common errors, including HTTP 503, HTTP 429, and the 400 Bad Request error.




